Another Atmospheric River Soaks Northern California
Special Stories
12 Apr 2018 8:06 AM
From NOAA by Tom Di Liberto
An unusual April storm system brought heavy rains to northern California during the beginning of the month. The soaking rains caused localized flooding and even melted some higher elevation snow, but also filled reservoirs in northern parts of the state.
The image above shows the total precipitable water forecast to be in the atmosphere at 11 a.m. on the West Coast on April 6 using data from the Global Forecast System model run. What is precipitable water? It is an estimate of how much water would be present if you could snap your fingers and turn all of the water vapor in the column of air above your head into liquid.
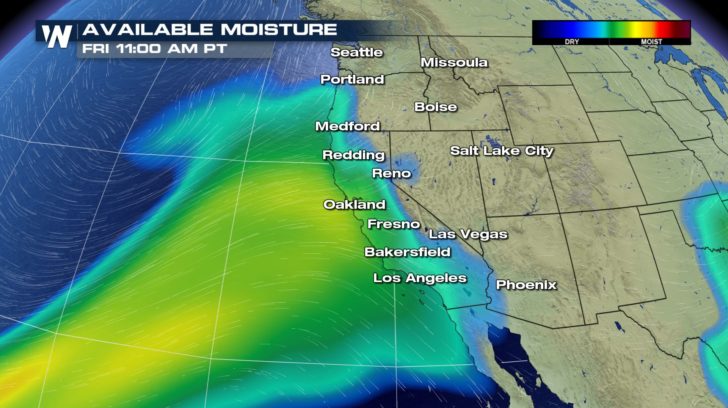 [The forecast Precipitable Water from Friday, April 6 where greens and yellows show the higher amounts of 'Pwat.']
The darker blue colors in the image show where the atmosphere was chock full of moisture, while blacker areas were regions where the atmosphere was dry. The atmosphere above the tropical Pacific is packed with moisture, but there is also a narrow bridge of moisture connecting the tropics and the West Coast of the United States. Bridges like these are known as atmospheric rivers, though they are sometimes called a “Pineapple Express” when the moisture flows from the area around Hawaii.
This event brought four to six inches of rain in 48 hours from April 6-7 across northern California. Most of the heaviest rains (more than six inches) fell along the northern Sierra Nevada Mountains, although coastal areas north of San Francisco also received around six inches. While there were reports of localized flooding, the rains were mostly helpful in filling reservoirs with water that will be used during the state’s dry summer months.
The West Coast experiences a handful of atmospheric river events each winter—the season during which California gets most of its precipitation. This atmospheric river was unusual not only for occurring in spring, but it also brought record-breaking moist air. Weather balloons launched from Oakland, California, measured the highest precipitable water amounts on record for any months from November through May.
[The forecast Precipitable Water from Friday, April 6 where greens and yellows show the higher amounts of 'Pwat.']
The darker blue colors in the image show where the atmosphere was chock full of moisture, while blacker areas were regions where the atmosphere was dry. The atmosphere above the tropical Pacific is packed with moisture, but there is also a narrow bridge of moisture connecting the tropics and the West Coast of the United States. Bridges like these are known as atmospheric rivers, though they are sometimes called a “Pineapple Express” when the moisture flows from the area around Hawaii.
This event brought four to six inches of rain in 48 hours from April 6-7 across northern California. Most of the heaviest rains (more than six inches) fell along the northern Sierra Nevada Mountains, although coastal areas north of San Francisco also received around six inches. While there were reports of localized flooding, the rains were mostly helpful in filling reservoirs with water that will be used during the state’s dry summer months.
The West Coast experiences a handful of atmospheric river events each winter—the season during which California gets most of its precipitation. This atmospheric river was unusual not only for occurring in spring, but it also brought record-breaking moist air. Weather balloons launched from Oakland, California, measured the highest precipitable water amounts on record for any months from November through May.
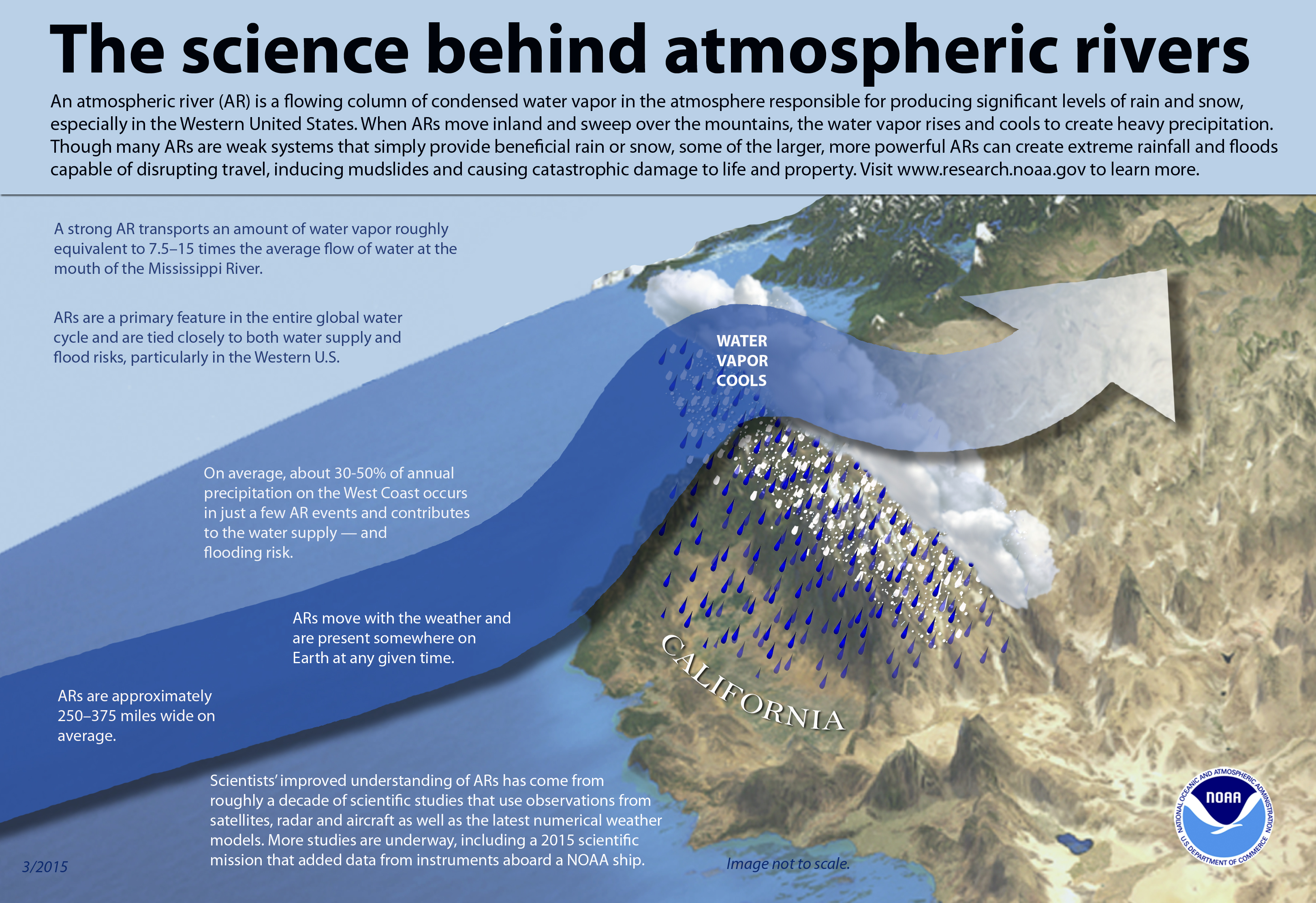 However, just because an atmospheric river brings record-moist air doesn’t guarantee it will generate record amounts of rain or snow. In this case, the atmosphere was able to squeeze out enough rain to set daily records in places like San Francisco.
Cities along the West Coast rely on atmospheric rivers to bring 30 to 50% of the total precipitation they may receive in a year. Because of their importance to regional water supplies, NOAA’s Climate Program Office devotes resources to studying atmospheric rivers. The goal of this research is not only to further our understanding of atmospheric rivers but better predict them weeks to months in advance and work with communities to help them make better use of predictions and warnings.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
However, just because an atmospheric river brings record-moist air doesn’t guarantee it will generate record amounts of rain or snow. In this case, the atmosphere was able to squeeze out enough rain to set daily records in places like San Francisco.
Cities along the West Coast rely on atmospheric rivers to bring 30 to 50% of the total precipitation they may receive in a year. Because of their importance to regional water supplies, NOAA’s Climate Program Office devotes resources to studying atmospheric rivers. The goal of this research is not only to further our understanding of atmospheric rivers but better predict them weeks to months in advance and work with communities to help them make better use of predictions and warnings.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
 [The forecast Precipitable Water from Friday, April 6 where greens and yellows show the higher amounts of 'Pwat.']
The darker blue colors in the image show where the atmosphere was chock full of moisture, while blacker areas were regions where the atmosphere was dry. The atmosphere above the tropical Pacific is packed with moisture, but there is also a narrow bridge of moisture connecting the tropics and the West Coast of the United States. Bridges like these are known as atmospheric rivers, though they are sometimes called a “Pineapple Express” when the moisture flows from the area around Hawaii.
This event brought four to six inches of rain in 48 hours from April 6-7 across northern California. Most of the heaviest rains (more than six inches) fell along the northern Sierra Nevada Mountains, although coastal areas north of San Francisco also received around six inches. While there were reports of localized flooding, the rains were mostly helpful in filling reservoirs with water that will be used during the state’s dry summer months.
The West Coast experiences a handful of atmospheric river events each winter—the season during which California gets most of its precipitation. This atmospheric river was unusual not only for occurring in spring, but it also brought record-breaking moist air. Weather balloons launched from Oakland, California, measured the highest precipitable water amounts on record for any months from November through May.
[The forecast Precipitable Water from Friday, April 6 where greens and yellows show the higher amounts of 'Pwat.']
The darker blue colors in the image show where the atmosphere was chock full of moisture, while blacker areas were regions where the atmosphere was dry. The atmosphere above the tropical Pacific is packed with moisture, but there is also a narrow bridge of moisture connecting the tropics and the West Coast of the United States. Bridges like these are known as atmospheric rivers, though they are sometimes called a “Pineapple Express” when the moisture flows from the area around Hawaii.
This event brought four to six inches of rain in 48 hours from April 6-7 across northern California. Most of the heaviest rains (more than six inches) fell along the northern Sierra Nevada Mountains, although coastal areas north of San Francisco also received around six inches. While there were reports of localized flooding, the rains were mostly helpful in filling reservoirs with water that will be used during the state’s dry summer months.
The West Coast experiences a handful of atmospheric river events each winter—the season during which California gets most of its precipitation. This atmospheric river was unusual not only for occurring in spring, but it also brought record-breaking moist air. Weather balloons launched from Oakland, California, measured the highest precipitable water amounts on record for any months from November through May.
 However, just because an atmospheric river brings record-moist air doesn’t guarantee it will generate record amounts of rain or snow. In this case, the atmosphere was able to squeeze out enough rain to set daily records in places like San Francisco.
Cities along the West Coast rely on atmospheric rivers to bring 30 to 50% of the total precipitation they may receive in a year. Because of their importance to regional water supplies, NOAA’s Climate Program Office devotes resources to studying atmospheric rivers. The goal of this research is not only to further our understanding of atmospheric rivers but better predict them weeks to months in advance and work with communities to help them make better use of predictions and warnings.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
However, just because an atmospheric river brings record-moist air doesn’t guarantee it will generate record amounts of rain or snow. In this case, the atmosphere was able to squeeze out enough rain to set daily records in places like San Francisco.
Cities along the West Coast rely on atmospheric rivers to bring 30 to 50% of the total precipitation they may receive in a year. Because of their importance to regional water supplies, NOAA’s Climate Program Office devotes resources to studying atmospheric rivers. The goal of this research is not only to further our understanding of atmospheric rivers but better predict them weeks to months in advance and work with communities to help them make better use of predictions and warnings.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More