Atmospheric Rivers Drive Western U.S. Flood Damages
Special Stories
23 Jan 2020 2:00 AM
[NOAA by Alison Stevens] New research recently published in Science Advances found that atmospheric rivers accounted for 84% of flood damages, or $42.6 billion, across the western United States from 1978-2017. Supported by NOAA's Regional Integrated Sciences and Assessments (RISA) and co-authored by California-Nevada RISA PI Alexander Gershunov, the study analyzed 40 years of data from the National Flood Insurance Program to quantify atmospheric rivers’ economic impacts.
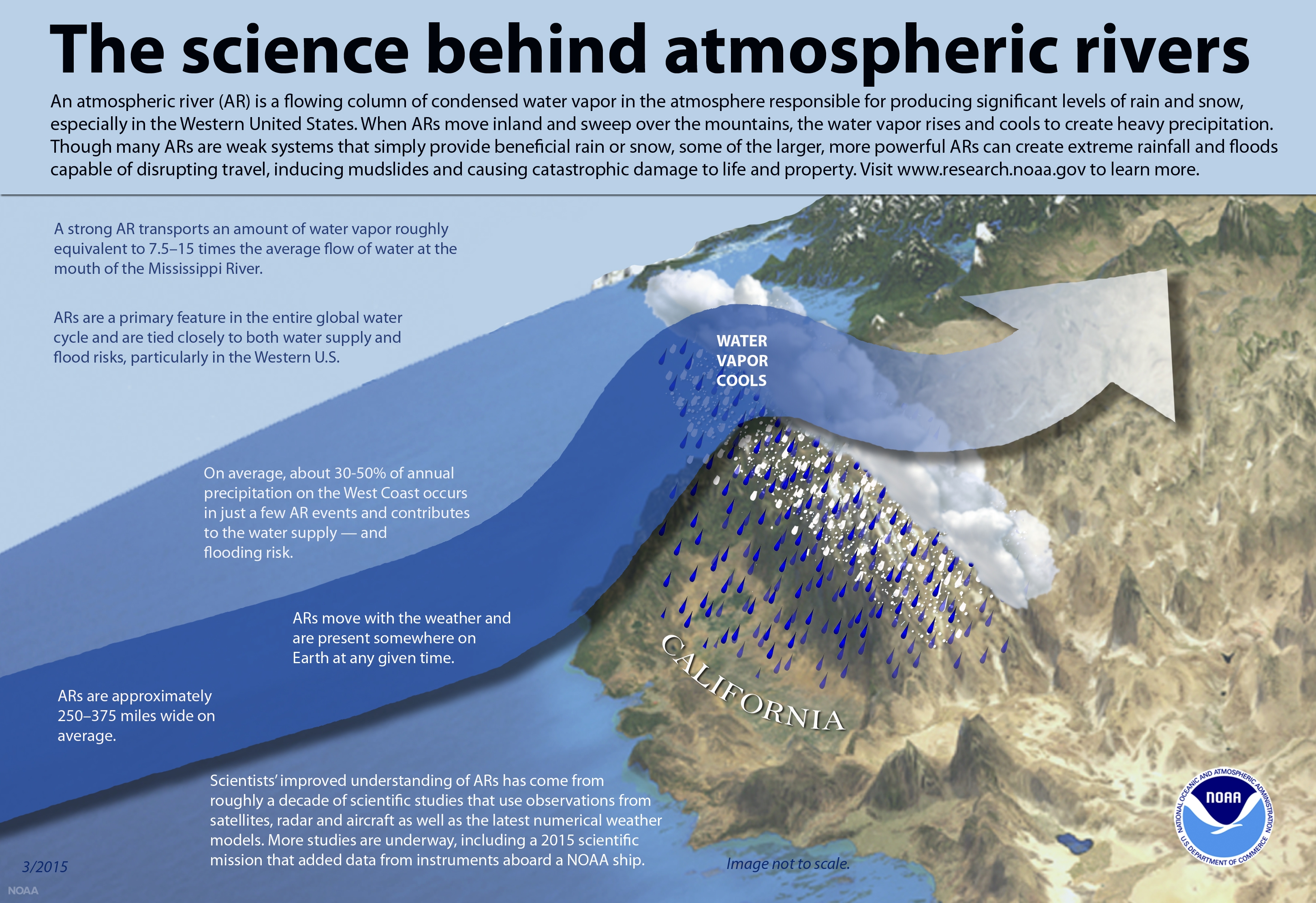 Not only were atmospheric rivers the primary driver across all 11 states, with annual average damages of $1.1 billion, but they also caused over 95% and even exceeded 99% of flood damages in some coastal areas of northern California and the Pacific Northwest.
In addition, the authors used a recently developed atmospheric rivers intensity and duration scale varying from 1 (weak) to 5 (exceptional) to assess how flood damages change with each category. They found that each increase in the atmospheric intensity and duration scale corresponds to a roughly 10-fold increase in flood damages. Flood damages from atmospheric rivers are expected to increase in the face of rising population, increased development, and climate change.
Not only were atmospheric rivers the primary driver across all 11 states, with annual average damages of $1.1 billion, but they also caused over 95% and even exceeded 99% of flood damages in some coastal areas of northern California and the Pacific Northwest.
In addition, the authors used a recently developed atmospheric rivers intensity and duration scale varying from 1 (weak) to 5 (exceptional) to assess how flood damages change with each category. They found that each increase in the atmospheric intensity and duration scale corresponds to a roughly 10-fold increase in flood damages. Flood damages from atmospheric rivers are expected to increase in the face of rising population, increased development, and climate change.
 Not only were atmospheric rivers the primary driver across all 11 states, with annual average damages of $1.1 billion, but they also caused over 95% and even exceeded 99% of flood damages in some coastal areas of northern California and the Pacific Northwest.
In addition, the authors used a recently developed atmospheric rivers intensity and duration scale varying from 1 (weak) to 5 (exceptional) to assess how flood damages change with each category. They found that each increase in the atmospheric intensity and duration scale corresponds to a roughly 10-fold increase in flood damages. Flood damages from atmospheric rivers are expected to increase in the face of rising population, increased development, and climate change.
Not only were atmospheric rivers the primary driver across all 11 states, with annual average damages of $1.1 billion, but they also caused over 95% and even exceeded 99% of flood damages in some coastal areas of northern California and the Pacific Northwest.
In addition, the authors used a recently developed atmospheric rivers intensity and duration scale varying from 1 (weak) to 5 (exceptional) to assess how flood damages change with each category. They found that each increase in the atmospheric intensity and duration scale corresponds to a roughly 10-fold increase in flood damages. Flood damages from atmospheric rivers are expected to increase in the face of rising population, increased development, and climate change. All Weather News
More