Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai Volcanic Eruption
Special Stories
19 Jan 2022 6:36 PM
NEAR TONGA | On January 14th and January 15, 2022 an underwater volcano erupted near Tonga sending a plume of ash, gas and steam upwards of 30 km (~18.6 mi) into the atmosphere and tsunami waves across the Pacific Ocean. Prior eruptions had been reported in December 2021.
[embed]https://twitter.com/NWSHonolulu/status/1482259099458932737?s=20[/embed]
According to experts, this was likely the biggest eruption recorded on planet Earth over the last 30 years and sent shockwaves across the planet.
Tsunami advisories were issued for many including the states of Alaska, Hawaii and the U.S. West Coast. The National Weather Service in San Diego, California was under a tsunami advisory for tsunami waves of 1-2 feet. This was to be added on top of normal wave heights of 4 feet plus the tsunami wave highs of 1-2 feet, meaning waves up to 5-6 feet were to be expected. Actual reports of 3 to 4 feet were observed.
[embed]https://twitter.com/NWSSanDiego/status/1482403489376395267?s=20[/embed]
According to NOAA, in December 2014 and January 2015 an underwater volcano near Tonga erupted creating a newly formed island between the two previously separate islands. Images of the islands seen from scientists below (via Planet), show satellite images of the island before and after the 2022 eruption.
[embed]https://twitter.com/tanyaofmars/status/1483560804226109444?s=20[/embed]
Satellite images from GOES West, also know as GOES 17 also show plume from space during the time of the eruption.
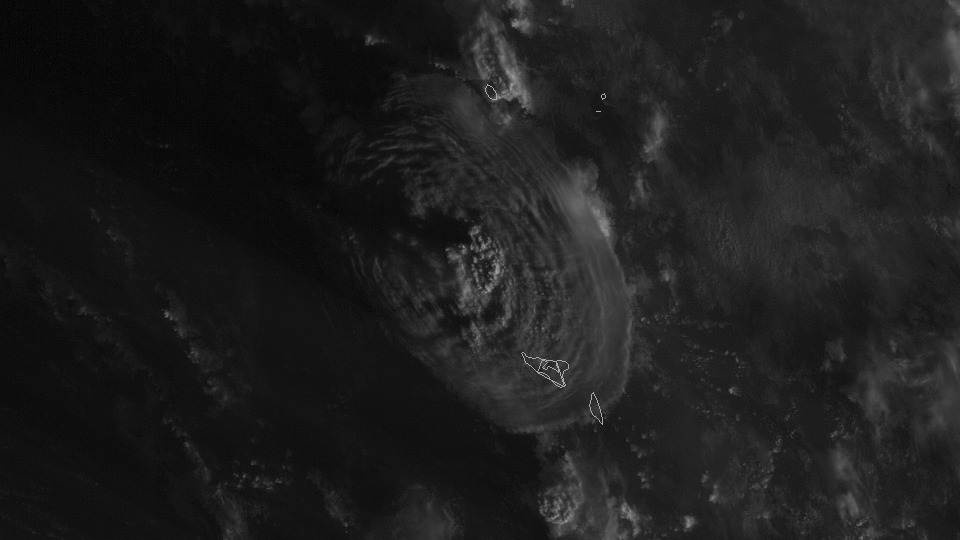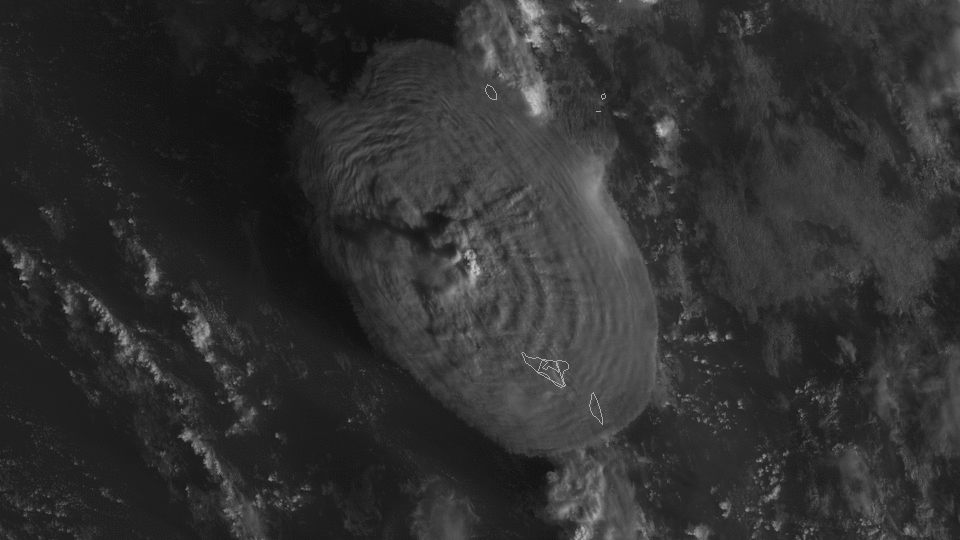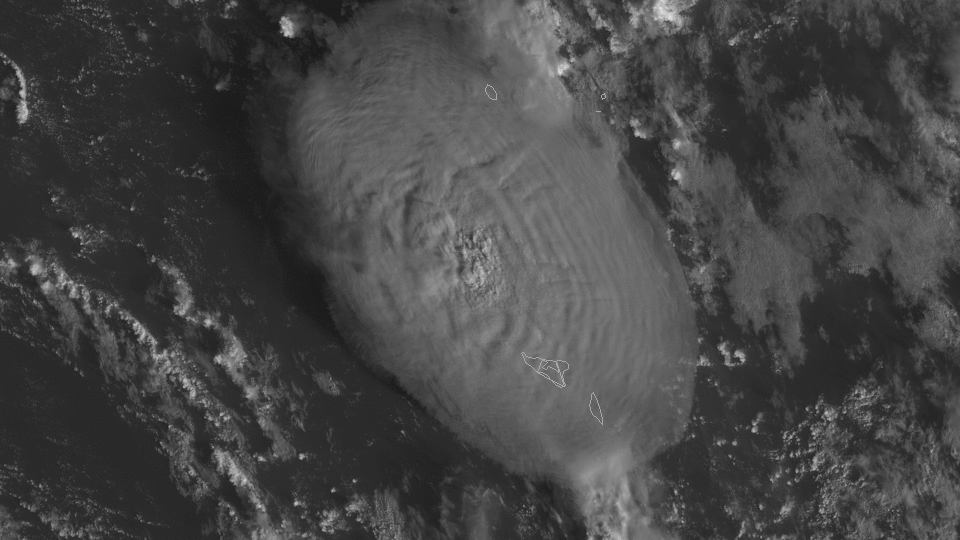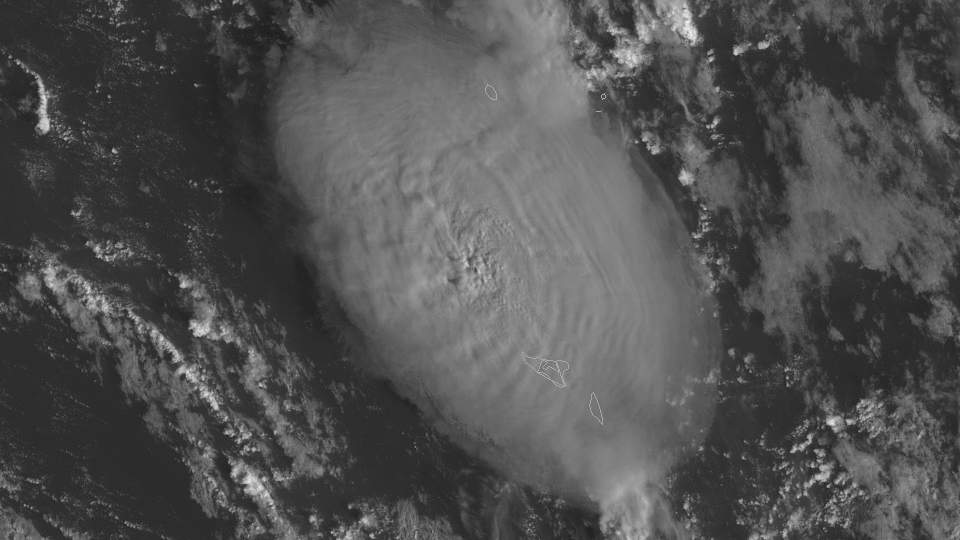 According to NASA researchers (source: NPR), the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai eruption was estimated to be 10 megatons of TNT equivalent. To put this into perspective, the Hiroshima nuclear bomb was approximately 15 kilotons.
[embed]https://twitter.com/NASAEarthData/status/1483468125794451462?s=20[/embed]
According to NASA researchers (source: NPR), the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai eruption was estimated to be 10 megatons of TNT equivalent. To put this into perspective, the Hiroshima nuclear bomb was approximately 15 kilotons.
[embed]https://twitter.com/NASAEarthData/status/1483468125794451462?s=20[/embed]
 According to NASA researchers (source: NPR), the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai eruption was estimated to be 10 megatons of TNT equivalent. To put this into perspective, the Hiroshima nuclear bomb was approximately 15 kilotons.
[embed]https://twitter.com/NASAEarthData/status/1483468125794451462?s=20[/embed]
According to NASA researchers (source: NPR), the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai eruption was estimated to be 10 megatons of TNT equivalent. To put this into perspective, the Hiroshima nuclear bomb was approximately 15 kilotons.
[embed]https://twitter.com/NASAEarthData/status/1483468125794451462?s=20[/embed]
How will this affect the weather?
The amount of sulfur dioxide these plumes sent into the atmosphere was not enough to globally cool the planet, according to NOAA scientists as well as the research observed in the scientific community of twitter: [embed]https://twitter.com/simoncarn/status/1482894801813098505?s=20[/embed] When volcanoes erupt, the ash plumes are composed of sulfate aerosols. These aerosols are reflective and scatter sunlights. If there are enough aerosols, sunlight is scattered back to space and thus cools the planet.All Weather News
More