The Key Triggers of 2017's Costly Western Wildfire Season
Special Stories
6 Jun 2018 7:31 AM
[The Thomas Fire from 2017. Credit: NASA Earth Observatory]
From University of Colorado Boulder
New research from University of Colorado in Boulder shows that three major “switches” affecting wildfire—fuel, aridity and ignition—were either flipped on and/or kept on longer than expected last year, triggering one of the largest and costliest U.S. wildfire seasons in recent decades.
The 2017 wildfire season cost the United States more than $18 billion in damages. That year, 71,000 wildfires scorched 10 million acres of land, destroying 12,000 homes, evacuating 200,000 people and claiming 66 lives. By comparison, 2016 saw 5.4 million acres burned.
“Last year, we saw a pile-on of extreme events across large portions of the western U.S: the wettest winter, the hottest summer and the driest fall—all helping to promote wildfires,” said lead study author Jennifer Balch, director of CU Boulder’s Earth Lab in the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES).
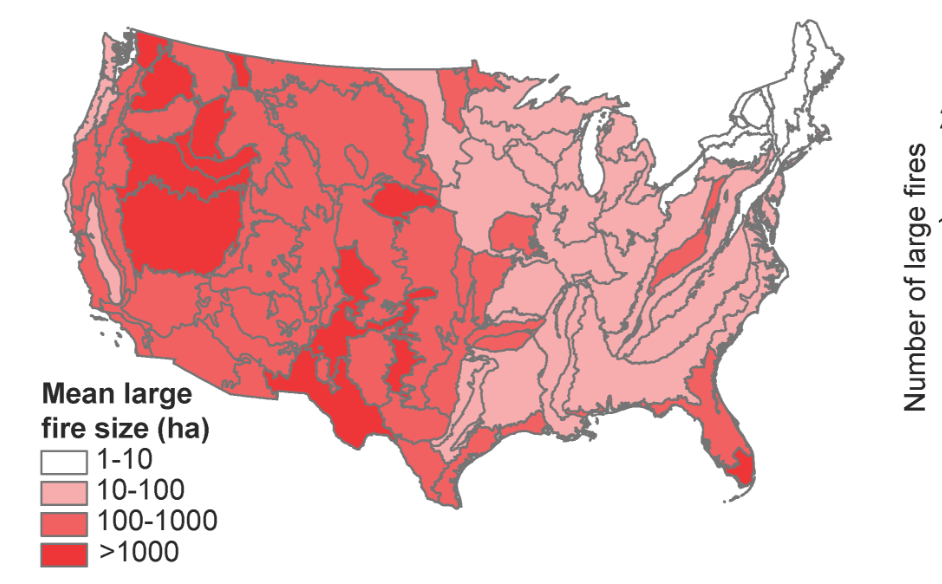 [Large fire size and relative sizes of human vs. lighting fires across ecoregions of the continental U.S. (a) The mean size of a large fire (top 10% of largest fires relative to the ecoregion) varies by three orders of magnitude across the continental U.S]
The new paper co-authored by researchers at CU Boulder’s Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research (INSTAAR), Columbia University and the University of Idaho was published this week in the journal Fire.
Western wildfire seasons are worse when conditions are dry and fuel-rich, raising the chances of ignition. The research team sought to pinpoint the precursors that led to 2017’s fires in order to provide information for decision makers considering policies that might prevent or minimize future fire disasters.
2017’s wet winter acted as the first trigger. Increased precipitation early in the year fed the growth of fine grasses across the western United States—grasses that would later serve as fuel for fire. Then, summer and fall brought dry, arid conditions, baking the dense fields of grasses into dehydrated kindling.
[Large fire size and relative sizes of human vs. lighting fires across ecoregions of the continental U.S. (a) The mean size of a large fire (top 10% of largest fires relative to the ecoregion) varies by three orders of magnitude across the continental U.S]
The new paper co-authored by researchers at CU Boulder’s Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research (INSTAAR), Columbia University and the University of Idaho was published this week in the journal Fire.
Western wildfire seasons are worse when conditions are dry and fuel-rich, raising the chances of ignition. The research team sought to pinpoint the precursors that led to 2017’s fires in order to provide information for decision makers considering policies that might prevent or minimize future fire disasters.
2017’s wet winter acted as the first trigger. Increased precipitation early in the year fed the growth of fine grasses across the western United States—grasses that would later serve as fuel for fire. Then, summer and fall brought dry, arid conditions, baking the dense fields of grasses into dehydrated kindling.
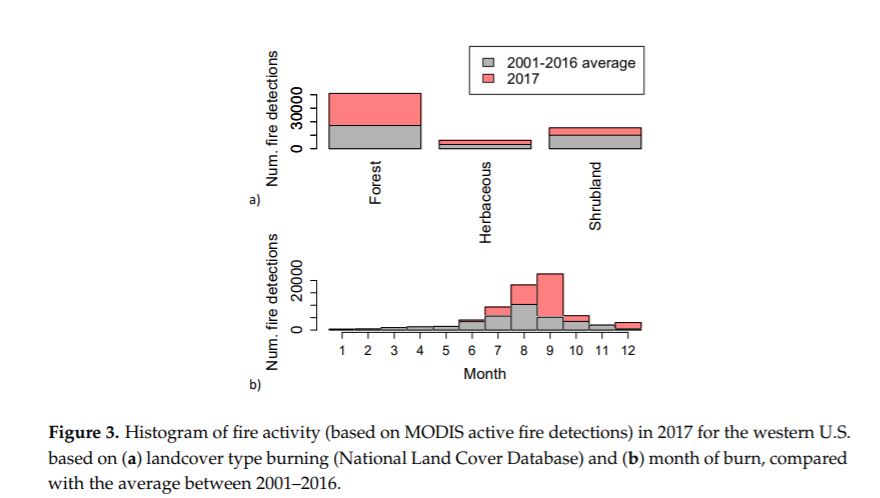 The scene was set for the third switch: ignition. Nearly 90 percent of total wildfires last year were sparked by people; Balch’s previous work has illuminated just how extensively humans exacerbate wildfire. Human activity triples the length of the average fire season.
”We expect to see more fire seasons like we saw last year,” said Megan Cattau, an Earth Lab researcher and a co-author on the study. “Thus, it is becoming increasingly critical that we strengthen our wildfire prediction and warning systems, support suppression and recovery efforts and develop sustained policies that help us coexist with fire.”
The paper notes that computer climate models project an increased risk of extreme wet winters in California and a decrease in summer precipitation across the entire West Coast. Those models also tend to project a delay in the onset of fall rain and snow.
The scene was set for the third switch: ignition. Nearly 90 percent of total wildfires last year were sparked by people; Balch’s previous work has illuminated just how extensively humans exacerbate wildfire. Human activity triples the length of the average fire season.
”We expect to see more fire seasons like we saw last year,” said Megan Cattau, an Earth Lab researcher and a co-author on the study. “Thus, it is becoming increasingly critical that we strengthen our wildfire prediction and warning systems, support suppression and recovery efforts and develop sustained policies that help us coexist with fire.”
The paper notes that computer climate models project an increased risk of extreme wet winters in California and a decrease in summer precipitation across the entire West Coast. Those models also tend to project a delay in the onset of fall rain and snow.
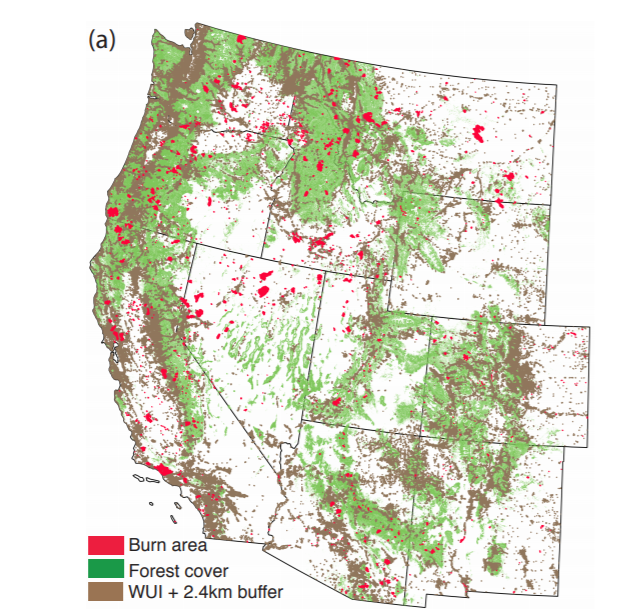 Although naturally occurring climate variability influences environmental conditions that affect the wildfire season, that variation is superimposed on an anthropogenically warmer world, so climate change is magnifying the effects of heat and precipitation extremes, Balch said.
“The 2018 wildfire season is already underway and here at home in the southern Rockies, fuels are very dry,” said Balch. “June is forecasted to be a busy month in terms of wildfires due to severe drought and low snowpack.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
Although naturally occurring climate variability influences environmental conditions that affect the wildfire season, that variation is superimposed on an anthropogenically warmer world, so climate change is magnifying the effects of heat and precipitation extremes, Balch said.
“The 2018 wildfire season is already underway and here at home in the southern Rockies, fuels are very dry,” said Balch. “June is forecasted to be a busy month in terms of wildfires due to severe drought and low snowpack.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
 [Large fire size and relative sizes of human vs. lighting fires across ecoregions of the continental U.S. (a) The mean size of a large fire (top 10% of largest fires relative to the ecoregion) varies by three orders of magnitude across the continental U.S]
The new paper co-authored by researchers at CU Boulder’s Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research (INSTAAR), Columbia University and the University of Idaho was published this week in the journal Fire.
Western wildfire seasons are worse when conditions are dry and fuel-rich, raising the chances of ignition. The research team sought to pinpoint the precursors that led to 2017’s fires in order to provide information for decision makers considering policies that might prevent or minimize future fire disasters.
2017’s wet winter acted as the first trigger. Increased precipitation early in the year fed the growth of fine grasses across the western United States—grasses that would later serve as fuel for fire. Then, summer and fall brought dry, arid conditions, baking the dense fields of grasses into dehydrated kindling.
[Large fire size and relative sizes of human vs. lighting fires across ecoregions of the continental U.S. (a) The mean size of a large fire (top 10% of largest fires relative to the ecoregion) varies by three orders of magnitude across the continental U.S]
The new paper co-authored by researchers at CU Boulder’s Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research (INSTAAR), Columbia University and the University of Idaho was published this week in the journal Fire.
Western wildfire seasons are worse when conditions are dry and fuel-rich, raising the chances of ignition. The research team sought to pinpoint the precursors that led to 2017’s fires in order to provide information for decision makers considering policies that might prevent or minimize future fire disasters.
2017’s wet winter acted as the first trigger. Increased precipitation early in the year fed the growth of fine grasses across the western United States—grasses that would later serve as fuel for fire. Then, summer and fall brought dry, arid conditions, baking the dense fields of grasses into dehydrated kindling.
 The scene was set for the third switch: ignition. Nearly 90 percent of total wildfires last year were sparked by people; Balch’s previous work has illuminated just how extensively humans exacerbate wildfire. Human activity triples the length of the average fire season.
”We expect to see more fire seasons like we saw last year,” said Megan Cattau, an Earth Lab researcher and a co-author on the study. “Thus, it is becoming increasingly critical that we strengthen our wildfire prediction and warning systems, support suppression and recovery efforts and develop sustained policies that help us coexist with fire.”
The paper notes that computer climate models project an increased risk of extreme wet winters in California and a decrease in summer precipitation across the entire West Coast. Those models also tend to project a delay in the onset of fall rain and snow.
The scene was set for the third switch: ignition. Nearly 90 percent of total wildfires last year were sparked by people; Balch’s previous work has illuminated just how extensively humans exacerbate wildfire. Human activity triples the length of the average fire season.
”We expect to see more fire seasons like we saw last year,” said Megan Cattau, an Earth Lab researcher and a co-author on the study. “Thus, it is becoming increasingly critical that we strengthen our wildfire prediction and warning systems, support suppression and recovery efforts and develop sustained policies that help us coexist with fire.”
The paper notes that computer climate models project an increased risk of extreme wet winters in California and a decrease in summer precipitation across the entire West Coast. Those models also tend to project a delay in the onset of fall rain and snow.
 Although naturally occurring climate variability influences environmental conditions that affect the wildfire season, that variation is superimposed on an anthropogenically warmer world, so climate change is magnifying the effects of heat and precipitation extremes, Balch said.
“The 2018 wildfire season is already underway and here at home in the southern Rockies, fuels are very dry,” said Balch. “June is forecasted to be a busy month in terms of wildfires due to severe drought and low snowpack.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
Although naturally occurring climate variability influences environmental conditions that affect the wildfire season, that variation is superimposed on an anthropogenically warmer world, so climate change is magnifying the effects of heat and precipitation extremes, Balch said.
“The 2018 wildfire season is already underway and here at home in the southern Rockies, fuels are very dry,” said Balch. “June is forecasted to be a busy month in terms of wildfires due to severe drought and low snowpack.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More