What Is An Inversion?
Special Stories
9 Dec 2020 9:34 AM
You may hear us occasionally throw the term "inversion" around here on WeatherNation, but what does it mean exactly? Well, let's take an example from Wednesday morning the 9th of December.
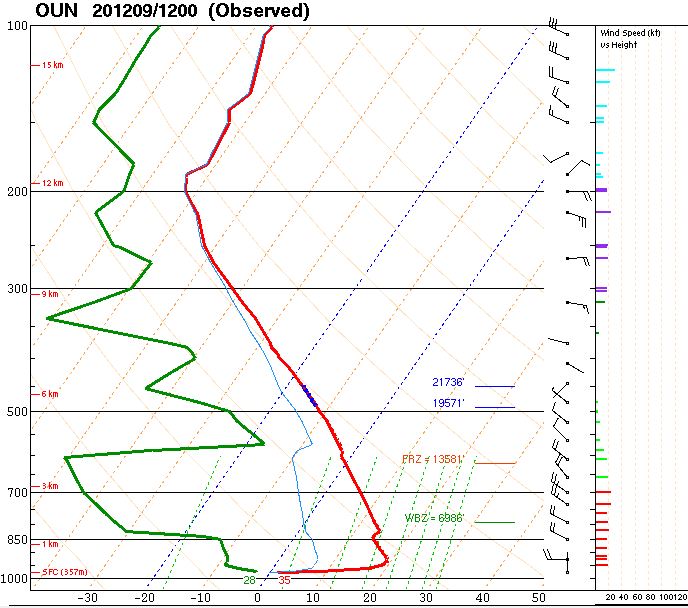 The weather balloon "sounding" [aka launch] from Norman, OK Dec 9, 2020. Red shows temperature, green shows dew point, and wind barbs are on the right. The chart shows ground level (bottom) to the top of the troposphere (top)Wednesday morning's weather balloon launch in central Oklahoma showed a distinct inversion. Take a look at the red line, pictured above. That red line represents the air temperature from the ground level (bottom of the graph) to the top of the troposphere (near the horizontal 200 line). You're looking at a Skew-T diagram, commonly used in weather observation and prediction by meteorologists. We want to point out the very bottom part of that red line. Look where it says 35, that means it was 35 degrees at ground level when the weather balloon was launched. The red line then jumps to the right, meaning the temperature rapidly rose as the weather balloon floated upward through the sky. Here is the raw data of the lowest level of the atmosphere:
The weather balloon "sounding" [aka launch] from Norman, OK Dec 9, 2020. Red shows temperature, green shows dew point, and wind barbs are on the right. The chart shows ground level (bottom) to the top of the troposphere (top)Wednesday morning's weather balloon launch in central Oklahoma showed a distinct inversion. Take a look at the red line, pictured above. That red line represents the air temperature from the ground level (bottom of the graph) to the top of the troposphere (near the horizontal 200 line). You're looking at a Skew-T diagram, commonly used in weather observation and prediction by meteorologists. We want to point out the very bottom part of that red line. Look where it says 35, that means it was 35 degrees at ground level when the weather balloon was launched. The red line then jumps to the right, meaning the temperature rapidly rose as the weather balloon floated upward through the sky. Here is the raw data of the lowest level of the atmosphere:
 File image of a weather balloon launch, courtesy the National Weather Service. Dozens of locations across the country release at least two weather balloons each day, one in the morning and one in the evening. The balloon rises and collects weather data through the troposphere.
Let's take a look at another example of a strong inversion Wednesday, this time in Dodge City, Kansas.
File image of a weather balloon launch, courtesy the National Weather Service. Dozens of locations across the country release at least two weather balloons each day, one in the morning and one in the evening. The balloon rises and collects weather data through the troposphere.
Let's take a look at another example of a strong inversion Wednesday, this time in Dodge City, Kansas.
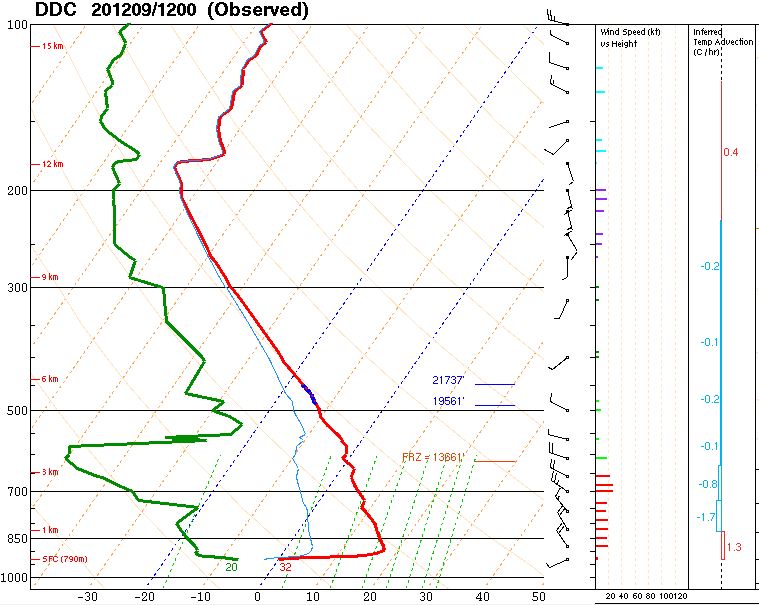 The weather balloon launch weather information from Dodge City, KS on Wednesday, December 9
The temperature inversion was not as strong as Norman's Wednesday, but it was still rather impressive. The temperature *rose* 32 degrees from ground level to 1,040 feet above the surface.
Why are temperature inversions important?
The weather balloon launch weather information from Dodge City, KS on Wednesday, December 9
The temperature inversion was not as strong as Norman's Wednesday, but it was still rather impressive. The temperature *rose* 32 degrees from ground level to 1,040 feet above the surface.
Why are temperature inversions important?
 An inversion layer's impact on air quality, smoke, haze, and fog.
An inversion is important when it comes to poor air quality, smoke, fog, and haze. When the temperature is hotter above the ground, it puts a "lid" on the atmosphere where the cool air near the surface cannot escape. That means the air sits still and that can lead to very poor air quality.
An inversion layer's impact on air quality, smoke, haze, and fog.
An inversion is important when it comes to poor air quality, smoke, fog, and haze. When the temperature is hotter above the ground, it puts a "lid" on the atmosphere where the cool air near the surface cannot escape. That means the air sits still and that can lead to very poor air quality.
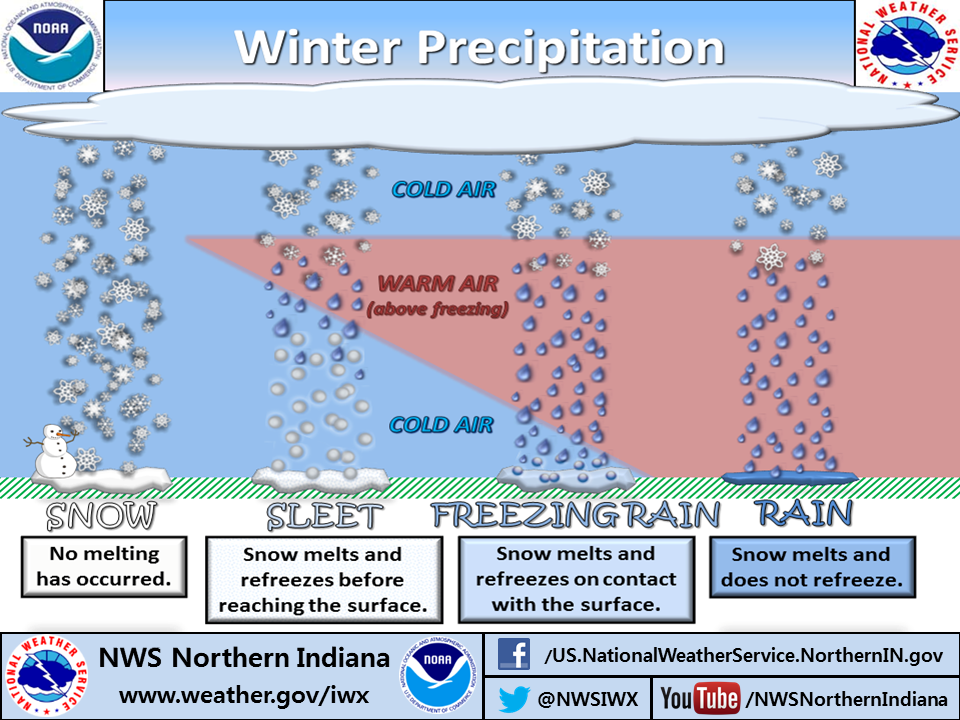 An example of an inversion's impact on precipitation type
Inversions play a critical role in winter precipitation type and predicting what kind of precipitation will fall at your location. Warmer air, above freezing, above the surface throws a wrench in precipitation because it oftentimes results in freezing rain or sleet (depending on how much warm air is there).
An example of an inversion's impact on precipitation type
Inversions play a critical role in winter precipitation type and predicting what kind of precipitation will fall at your location. Warmer air, above freezing, above the surface throws a wrench in precipitation because it oftentimes results in freezing rain or sleet (depending on how much warm air is there).
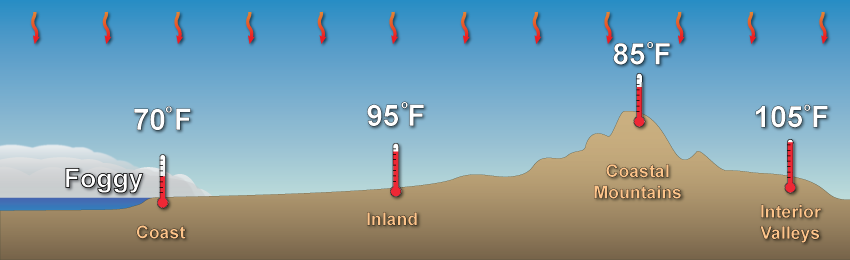 Inversion layers when it comes to marine layers
When coastal areas, such as California, get a marine layer it results in an inversion. The cool, dense air stays near the surface while the mountains stay warmer and drier. This can be important in forecasting how long a marine layer my linger.
Finally, an interesting result of inversions:
Inversion layers when it comes to marine layers
When coastal areas, such as California, get a marine layer it results in an inversion. The cool, dense air stays near the surface while the mountains stay warmer and drier. This can be important in forecasting how long a marine layer my linger.
Finally, an interesting result of inversions:
 An inversion's impact on sound.
An inversion can also lead to louder noises, because the sound travels and then bounces off that warmer layer above the surface, bounces back and results in some noisier surroundings!
Please share this article if you've found it useful!
An inversion's impact on sound.
An inversion can also lead to louder noises, because the sound travels and then bounces off that warmer layer above the surface, bounces back and results in some noisier surroundings!
Please share this article if you've found it useful!
 The weather balloon "sounding" [aka launch] from Norman, OK Dec 9, 2020. Red shows temperature, green shows dew point, and wind barbs are on the right. The chart shows ground level (bottom) to the top of the troposphere (top)Wednesday morning's weather balloon launch in central Oklahoma showed a distinct inversion. Take a look at the red line, pictured above. That red line represents the air temperature from the ground level (bottom of the graph) to the top of the troposphere (near the horizontal 200 line). You're looking at a Skew-T diagram, commonly used in weather observation and prediction by meteorologists. We want to point out the very bottom part of that red line. Look where it says 35, that means it was 35 degrees at ground level when the weather balloon was launched. The red line then jumps to the right, meaning the temperature rapidly rose as the weather balloon floated upward through the sky. Here is the raw data of the lowest level of the atmosphere:
The weather balloon "sounding" [aka launch] from Norman, OK Dec 9, 2020. Red shows temperature, green shows dew point, and wind barbs are on the right. The chart shows ground level (bottom) to the top of the troposphere (top)Wednesday morning's weather balloon launch in central Oklahoma showed a distinct inversion. Take a look at the red line, pictured above. That red line represents the air temperature from the ground level (bottom of the graph) to the top of the troposphere (near the horizontal 200 line). You're looking at a Skew-T diagram, commonly used in weather observation and prediction by meteorologists. We want to point out the very bottom part of that red line. Look where it says 35, that means it was 35 degrees at ground level when the weather balloon was launched. The red line then jumps to the right, meaning the temperature rapidly rose as the weather balloon floated upward through the sky. Here is the raw data of the lowest level of the atmosphere:
- Ground level, Norman: 35 degrees
- 130 feet above ground: 48 degrees
- 440 feet above ground: 63 degrees
 File image of a weather balloon launch, courtesy the National Weather Service. Dozens of locations across the country release at least two weather balloons each day, one in the morning and one in the evening. The balloon rises and collects weather data through the troposphere.
Let's take a look at another example of a strong inversion Wednesday, this time in Dodge City, Kansas.
File image of a weather balloon launch, courtesy the National Weather Service. Dozens of locations across the country release at least two weather balloons each day, one in the morning and one in the evening. The balloon rises and collects weather data through the troposphere.
Let's take a look at another example of a strong inversion Wednesday, this time in Dodge City, Kansas.
 The weather balloon launch weather information from Dodge City, KS on Wednesday, December 9
The temperature inversion was not as strong as Norman's Wednesday, but it was still rather impressive. The temperature *rose* 32 degrees from ground level to 1,040 feet above the surface.
Why are temperature inversions important?
The weather balloon launch weather information from Dodge City, KS on Wednesday, December 9
The temperature inversion was not as strong as Norman's Wednesday, but it was still rather impressive. The temperature *rose* 32 degrees from ground level to 1,040 feet above the surface.
Why are temperature inversions important?
 An inversion layer's impact on air quality, smoke, haze, and fog.
An inversion is important when it comes to poor air quality, smoke, fog, and haze. When the temperature is hotter above the ground, it puts a "lid" on the atmosphere where the cool air near the surface cannot escape. That means the air sits still and that can lead to very poor air quality.
An inversion layer's impact on air quality, smoke, haze, and fog.
An inversion is important when it comes to poor air quality, smoke, fog, and haze. When the temperature is hotter above the ground, it puts a "lid" on the atmosphere where the cool air near the surface cannot escape. That means the air sits still and that can lead to very poor air quality.
 An example of an inversion's impact on precipitation type
Inversions play a critical role in winter precipitation type and predicting what kind of precipitation will fall at your location. Warmer air, above freezing, above the surface throws a wrench in precipitation because it oftentimes results in freezing rain or sleet (depending on how much warm air is there).
An example of an inversion's impact on precipitation type
Inversions play a critical role in winter precipitation type and predicting what kind of precipitation will fall at your location. Warmer air, above freezing, above the surface throws a wrench in precipitation because it oftentimes results in freezing rain or sleet (depending on how much warm air is there).
 Inversion layers when it comes to marine layers
When coastal areas, such as California, get a marine layer it results in an inversion. The cool, dense air stays near the surface while the mountains stay warmer and drier. This can be important in forecasting how long a marine layer my linger.
Finally, an interesting result of inversions:
Inversion layers when it comes to marine layers
When coastal areas, such as California, get a marine layer it results in an inversion. The cool, dense air stays near the surface while the mountains stay warmer and drier. This can be important in forecasting how long a marine layer my linger.
Finally, an interesting result of inversions:
 An inversion's impact on sound.
An inversion can also lead to louder noises, because the sound travels and then bounces off that warmer layer above the surface, bounces back and results in some noisier surroundings!
Please share this article if you've found it useful!
An inversion's impact on sound.
An inversion can also lead to louder noises, because the sound travels and then bounces off that warmer layer above the surface, bounces back and results in some noisier surroundings!
Please share this article if you've found it useful!All Weather News
More