April El Nino Update: Alternative Communication
Special Stories
14 Apr 2020 2:00 AM
[Average sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies (°C) for the week centered on April 1st. Anomalies are computed with respect to the 1981-2010 base period weekly means. From NOAA]
[From NOAA written by Michelle L'Heureux]
It’s a new month, but it seems like an entirely different world as we peer at the tropical Pacific Ocean. Sea surface temperatures remained warmer than average, but the tropical atmosphere shifted away from its El Niño-ish appearance during February. The lack of coupling between the ocean and atmosphere leads forecasters to once again favor the continuation of ENSO-neutral with a ~60% chance during the summer, and remaining most likely during the autumn.
 It’s special because there isn’t an analogous streak, remaining right at +0.50°C, in the historical record going back to 1950. However, keep in mind that right now the “departure from average” is being computed relative to 1986-2015 seasonal averages. Eventually, because we roll the climatology forward in time, the current numbers will change when we update the reference (averaging) period to 1991-2020. Because sea surface temperatures are above average over most of the Tropics right now, suggesting that the updated 30-year average will be warmer than the 1986-2015 average, we are betting these historical index values will eventually be revised downwards.
However, we don’t just look at the ocean temperatures when we determine the status of ENSO—we also examine the atmospheric circulation over the tropical Pacific Ocean. Changes in the atmospheric circulation (especially the location of tropical rainfall) result in teleconnections that impact the climate over far-flung regions across the globe.
Other than some evidence in February, we have not seen persistent shifts in tropical rainfall, and March 2020 was no exception. In the past month, rainfall/cloudiness was near average-to-suppressed in the central tropical Pacific Ocean (during El Niño, there is typically increased rainfall/cloudiness in this region).
It’s special because there isn’t an analogous streak, remaining right at +0.50°C, in the historical record going back to 1950. However, keep in mind that right now the “departure from average” is being computed relative to 1986-2015 seasonal averages. Eventually, because we roll the climatology forward in time, the current numbers will change when we update the reference (averaging) period to 1991-2020. Because sea surface temperatures are above average over most of the Tropics right now, suggesting that the updated 30-year average will be warmer than the 1986-2015 average, we are betting these historical index values will eventually be revised downwards.
However, we don’t just look at the ocean temperatures when we determine the status of ENSO—we also examine the atmospheric circulation over the tropical Pacific Ocean. Changes in the atmospheric circulation (especially the location of tropical rainfall) result in teleconnections that impact the climate over far-flung regions across the globe.
Other than some evidence in February, we have not seen persistent shifts in tropical rainfall, and March 2020 was no exception. In the past month, rainfall/cloudiness was near average-to-suppressed in the central tropical Pacific Ocean (during El Niño, there is typically increased rainfall/cloudiness in this region).
 Stronger-than-average trade winds were also observed over the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, which is not typical of a reduced Walker circulation that would occur during El Nino. The Southern Oscillation indices remain near average as well. So, it appears the warm ocean is socially distant from its atmospheric dance partner.
Stronger-than-average trade winds were also observed over the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, which is not typical of a reduced Walker circulation that would occur during El Nino. The Southern Oscillation indices remain near average as well. So, it appears the warm ocean is socially distant from its atmospheric dance partner.
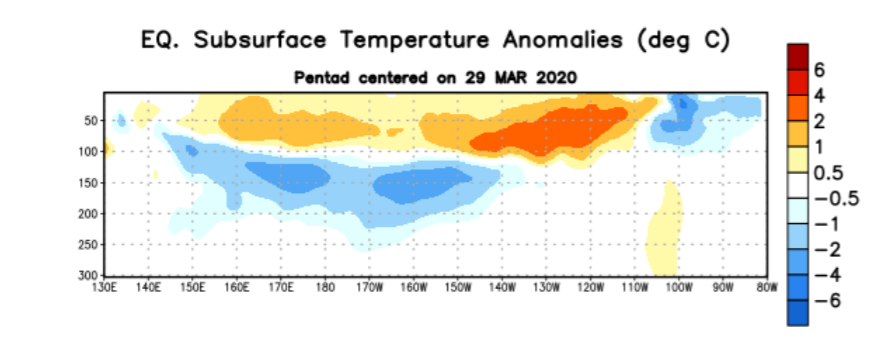 [Depth-longitude section of equatorial Pacific upper-ocean (0-300 meters) temperature anomalies (°C) centered on March 29th. Anomalies are departures from the 1981-2010 base period pentad means. From NOAA]
[Depth-longitude section of equatorial Pacific upper-ocean (0-300 meters) temperature anomalies (°C) centered on March 29th. Anomalies are departures from the 1981-2010 base period pentad means. From NOAA]
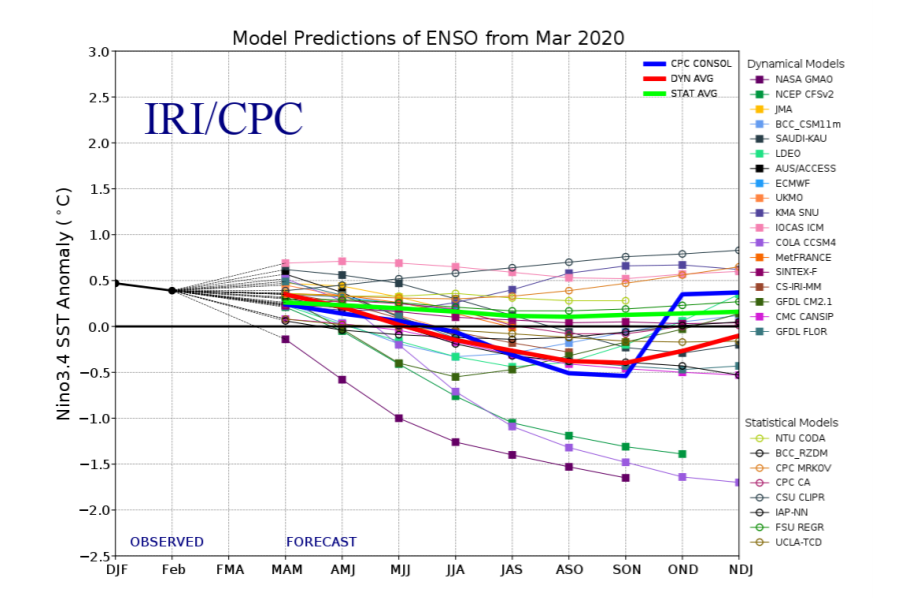 [Model forecasts of sea surface temperature anomalies for the Niño 3.4 region (5°N-5°S, 120°W-170°W). Figure updated March 19. From NOAA]
[Model forecasts of sea surface temperature anomalies for the Niño 3.4 region (5°N-5°S, 120°W-170°W). Figure updated March 19. From NOAA]
Share Your Screen
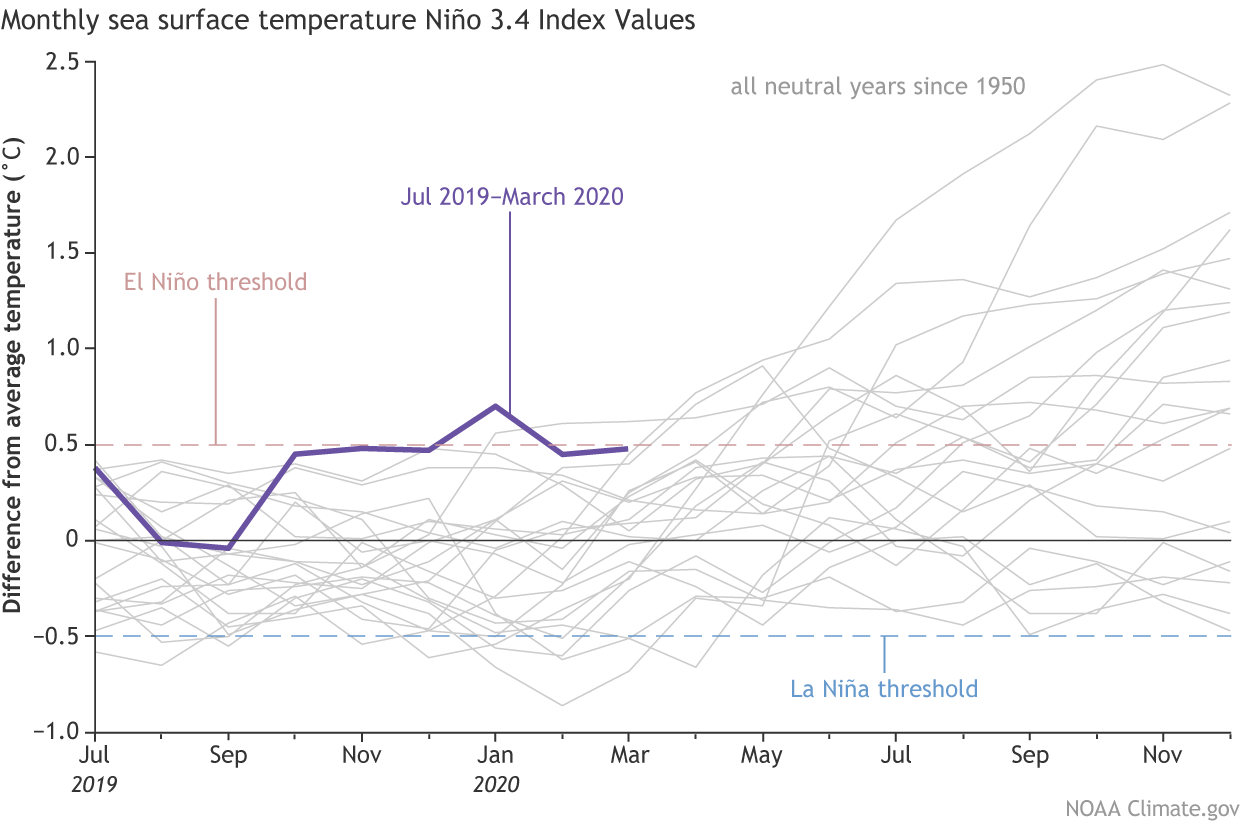
In the last month, ocean surface temperatures in the Niño-3.4 region have been bubbling around +0.5°C, our El Niño threshold. If you look at monthly averages in this region going back to October 2019, we’ve been between +0.45°C and +0.50°C for five of the six months! That’s pretty special!
[Monthly sea surface temperature in the Niño 3.4 region of the tropical Pacific for 2019-2020 (purple line) and all other years starting from neutral winters since 1950. NOAA Climate graph based on ERSSTv5 temperature data from NCEI.]

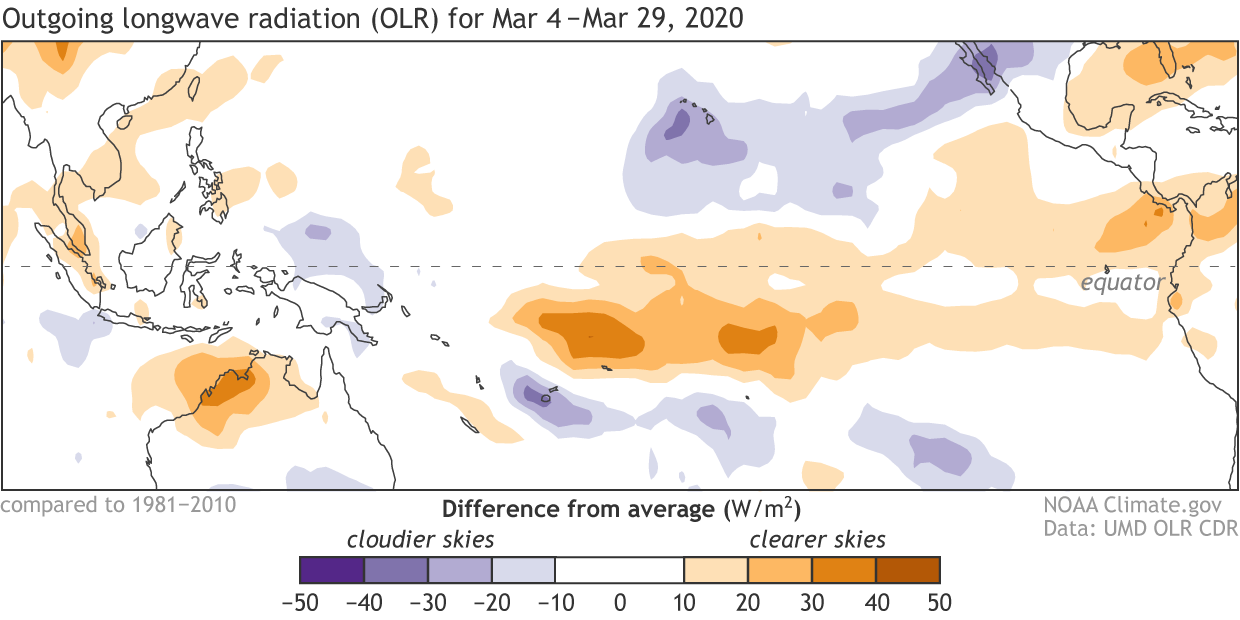
Places that were more (purple) or less (orange) cloudy than the 1981-2010 average during March 2020, based on satellite observations of OLR (outgoing longwave radiation, or heat). Thick clouds block heat from radiating out to space, so less radiation equals more clouds and rainfall, and more radiation equals clearer skies. The lack of clouds and rain resulting from the cooler-than-average side of the IOD can be seen on the left of this map. Climate.gov map from CPC data.
 [Depth-longitude section of equatorial Pacific upper-ocean (0-300 meters) temperature anomalies (°C) centered on March 29th. Anomalies are departures from the 1981-2010 base period pentad means. From NOAA]
[Depth-longitude section of equatorial Pacific upper-ocean (0-300 meters) temperature anomalies (°C) centered on March 29th. Anomalies are departures from the 1981-2010 base period pentad means. From NOAA]
Mute Your Audio
Model forecasts continue to indicate that ENSO-neutral conditions will persist through Northern Hemisphere summer and into the autumn of 2020. Forecasters are keeping one eye on a possible La Niña during the latter half of the year, which is reflected in the 30-40% chances. The “in house” NCEP Climate Forecast System (CFSv2) is one of the most bullish models to support development of La Niña, but there are many other state-of-the-art models that disagree, so forecasters are not putting much weight in it at this point. With that said, the spread of possible outcomes is still considerable and we are smack dab in the midst of the spring prediction barrier, which is when models tend to have lower skill or accuracy. Also, as Emily pointed out last month, it would be unusual for a La Niña to form after an ENSO-neutral winter. But as regular readers know, with only a small number of historical ENSO events to compare to (20-25 El Niño or La Niña episodes since 1950), “unusual” is often the norm! All the more reason to keep watching ENSO—each event or non-event is a learning experience. [Model forecasts of sea surface temperature anomalies for the Niño 3.4 region (5°N-5°S, 120°W-170°W). Figure updated March 19. From NOAA]
[Model forecasts of sea surface temperature anomalies for the Niño 3.4 region (5°N-5°S, 120°W-170°W). Figure updated March 19. From NOAA]All Weather News
More