NOAA Launches First Rip Current Forecast Model
Special Stories
13 May 2021 1:45 AM
[This image shows a rip current using a harmless green dye. Rip currents are powerful, narrow channels of fast-moving water that are prevalent along the East, Gulf, and West coasts of the U.S., as well as along the shores of the Great Lakes. Moving at speeds of up to eight feet per second, rip currents can move faster than an Olympic swimmer.]
[Written by NOAA] For the first time, NOAA is launching a national rip current forecast model, aimed at saving lives of beach-goers around the country. This new model can predict the hourly probability of rip currents along U.S. beaches up to six days out.
NOAA’s National Ocean Service and National Weather Service collaboratively developed and implemented the model, which leverages wave and water level information from the recently upgraded National Weather Service’s Nearshore Wave Prediction System. Similar to predicting weather or precipitation, the model predicts the likelihood of dangerous seaward currents on a sliding scale - from 0 to 100%.
 “Safety for beach-goers and boaters is taking a major leap forward with the launch of this new NOAA model,” said Nicole LeBoeuf, acting director of NOAA’s National Ocean Service. “Extending forecasting capabilities for dangerous rip currents out to six days provides forecasters and local authorities greater time to inform residents about the presence of this deadly beach hazard, thereby saving lives and protecting communities.”
“Improved model resolution will enable forecasters to issue more accurate and detailed rip current forecasts further into the future,” said Allison Allen, Chief, Marine, Tropical, and Tsunami Services Branch, NOAA’s National Weather Service. “This information enables public safety personnel to better prepare for hazardous beach conditions and inform the public of potential for danger before they head to the beach.”
“Safety for beach-goers and boaters is taking a major leap forward with the launch of this new NOAA model,” said Nicole LeBoeuf, acting director of NOAA’s National Ocean Service. “Extending forecasting capabilities for dangerous rip currents out to six days provides forecasters and local authorities greater time to inform residents about the presence of this deadly beach hazard, thereby saving lives and protecting communities.”
“Improved model resolution will enable forecasters to issue more accurate and detailed rip current forecasts further into the future,” said Allison Allen, Chief, Marine, Tropical, and Tsunami Services Branch, NOAA’s National Weather Service. “This information enables public safety personnel to better prepare for hazardous beach conditions and inform the public of potential for danger before they head to the beach.”
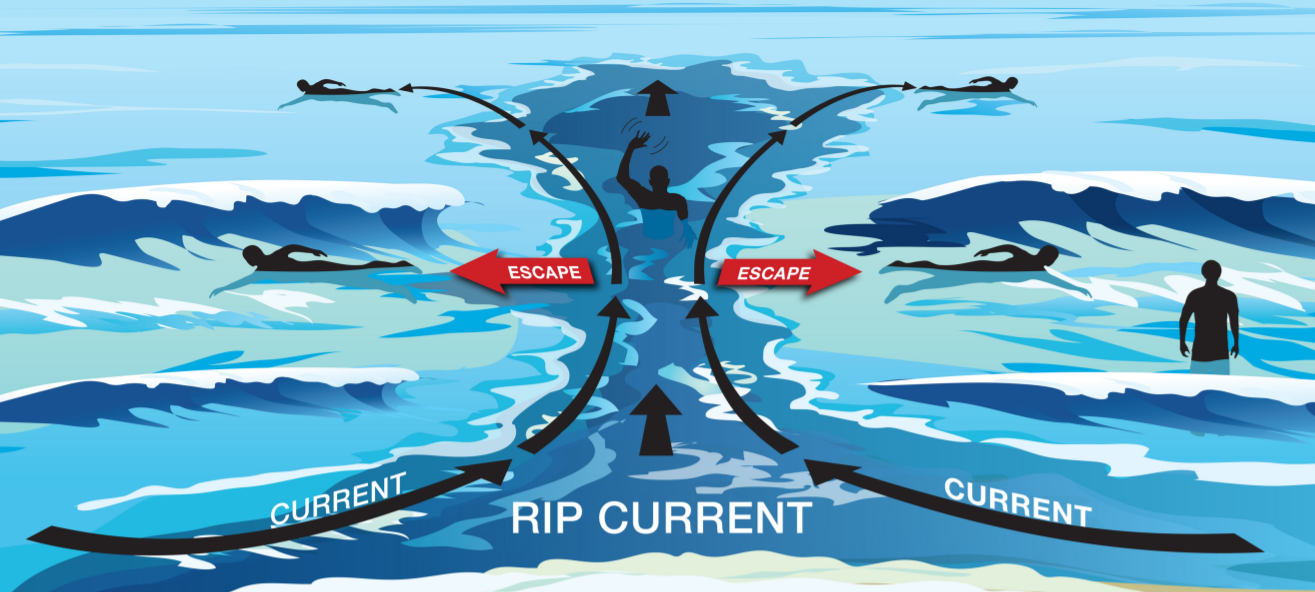 The forecast model covers a majority of the U.S. East and Gulf Coast and portions of California, Hawaii, Guam and Puerto Rico. Additional coastline coverage will be expanded in the future.
“Rip currents account for an estimated 100 deaths in the United States each year,” said Gregory Dusek, NOAA scientist who developed the model. “Before this, forecasters were manually predicting rip currents on a large section of the ocean twice a day and only a day or two into the future. The earlier prediction has potential to substantially increase awareness and reduce drownings.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace Michaels
The forecast model covers a majority of the U.S. East and Gulf Coast and portions of California, Hawaii, Guam and Puerto Rico. Additional coastline coverage will be expanded in the future.
“Rip currents account for an estimated 100 deaths in the United States each year,” said Gregory Dusek, NOAA scientist who developed the model. “Before this, forecasters were manually predicting rip currents on a large section of the ocean twice a day and only a day or two into the future. The earlier prediction has potential to substantially increase awareness and reduce drownings.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace Michaels
 “Safety for beach-goers and boaters is taking a major leap forward with the launch of this new NOAA model,” said Nicole LeBoeuf, acting director of NOAA’s National Ocean Service. “Extending forecasting capabilities for dangerous rip currents out to six days provides forecasters and local authorities greater time to inform residents about the presence of this deadly beach hazard, thereby saving lives and protecting communities.”
“Improved model resolution will enable forecasters to issue more accurate and detailed rip current forecasts further into the future,” said Allison Allen, Chief, Marine, Tropical, and Tsunami Services Branch, NOAA’s National Weather Service. “This information enables public safety personnel to better prepare for hazardous beach conditions and inform the public of potential for danger before they head to the beach.”
“Safety for beach-goers and boaters is taking a major leap forward with the launch of this new NOAA model,” said Nicole LeBoeuf, acting director of NOAA’s National Ocean Service. “Extending forecasting capabilities for dangerous rip currents out to six days provides forecasters and local authorities greater time to inform residents about the presence of this deadly beach hazard, thereby saving lives and protecting communities.”
“Improved model resolution will enable forecasters to issue more accurate and detailed rip current forecasts further into the future,” said Allison Allen, Chief, Marine, Tropical, and Tsunami Services Branch, NOAA’s National Weather Service. “This information enables public safety personnel to better prepare for hazardous beach conditions and inform the public of potential for danger before they head to the beach.”
 The forecast model covers a majority of the U.S. East and Gulf Coast and portions of California, Hawaii, Guam and Puerto Rico. Additional coastline coverage will be expanded in the future.
“Rip currents account for an estimated 100 deaths in the United States each year,” said Gregory Dusek, NOAA scientist who developed the model. “Before this, forecasters were manually predicting rip currents on a large section of the ocean twice a day and only a day or two into the future. The earlier prediction has potential to substantially increase awareness and reduce drownings.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace Michaels
The forecast model covers a majority of the U.S. East and Gulf Coast and portions of California, Hawaii, Guam and Puerto Rico. Additional coastline coverage will be expanded in the future.
“Rip currents account for an estimated 100 deaths in the United States each year,” said Gregory Dusek, NOAA scientist who developed the model. “Before this, forecasters were manually predicting rip currents on a large section of the ocean twice a day and only a day or two into the future. The earlier prediction has potential to substantially increase awareness and reduce drownings.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More