When Major Hurricanes Weaken to Tropical Storms, Study Shows Flooding Becomes the Biggest Threat
Special Stories
1 Jul 2020 2:00 AM
[Satellite imagery captures powerful major Hurricane Irma in September 2017. Courtesy: NASA and CIRA]
[From NOAA written by John Dos Passos Coggin] When a major hurricane approaching the United States relaxes to a tropical storm, people breathe a sigh of relief. But when it comes to extreme rain, this appears to be when they are most dangerous. In fact, new NOAA-funded research finds that across all major Atlantic hurricanes affecting the southeastern and eastern United States during the twentieth century, the largest areas and heaviest intensities of rainfall over land occur after major hurricanes become tropical storms, not during hurricanes or even major hurricanes.
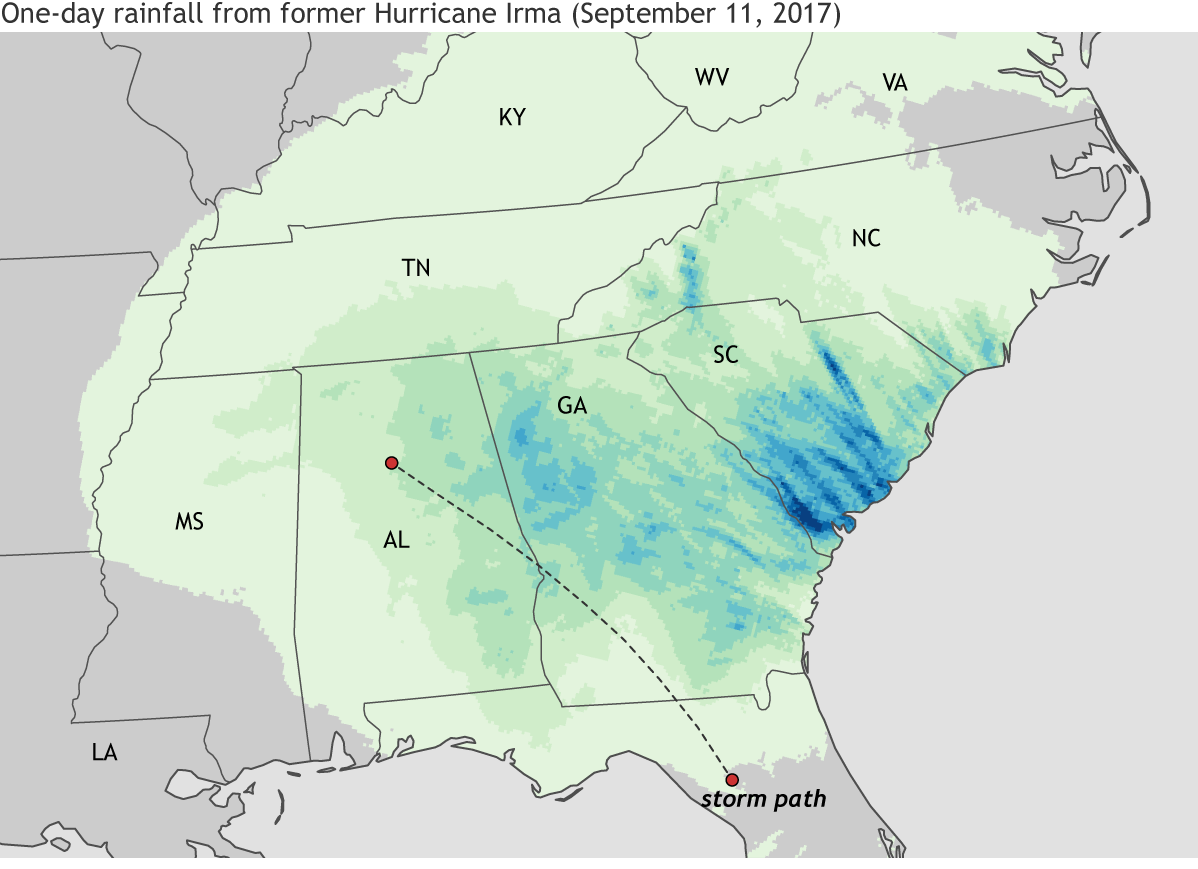
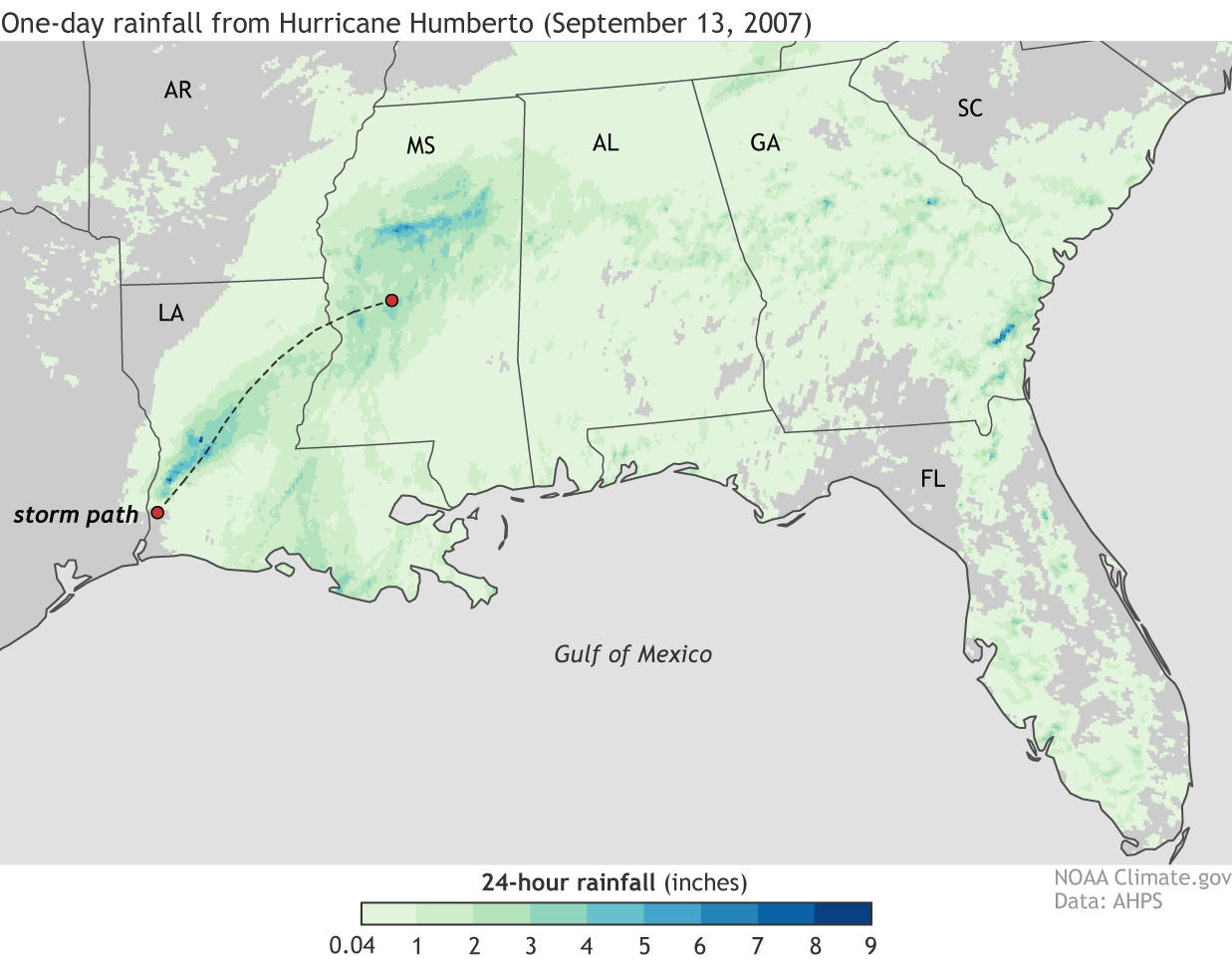 These rainfall maps offer an example of the somewhat counterintuitive pattern. The top map shows 24-hour total precipitation from former-Hurricane Irma on September 11, 2017, 12:00 UTC, when it was a tropical storm. The bottom map shows 24-hour rainfall totals from Hurricane Humberto on September 13, 2007, 12:00 UTC, while it was a hurricane. Darker colors indicate heavier precipitation. Irma as a tropical storm had a larger spatial extent and heavier rainfall—one-day totals were more than 5 inches across large parts of Georgia and South Carolina—than Humberto did as a landfalling hurricane.
The research team, which was funded by the NOAA Climate Program Office’s Modeling, Analysis, Predictions and Projections (MAPP) program, the Department of Energy, and Stanford University, used rainfall measurements from land-based weather stations dating back to the beginning of the twentieth century. They categorized Atlantic hurricanes affecting the southeastern and eastern United States based on both their lifetime maximum intensity and their intensity while they were raining over land. The researchers found that, on average, rainfall was most extreme in situations like Irma; tropical storms evolved from major hurricanes dumped heavier precipitation over a wider area than other types of storms—even hurricanes or major hurricanes.
These rainfall maps offer an example of the somewhat counterintuitive pattern. The top map shows 24-hour total precipitation from former-Hurricane Irma on September 11, 2017, 12:00 UTC, when it was a tropical storm. The bottom map shows 24-hour rainfall totals from Hurricane Humberto on September 13, 2007, 12:00 UTC, while it was a hurricane. Darker colors indicate heavier precipitation. Irma as a tropical storm had a larger spatial extent and heavier rainfall—one-day totals were more than 5 inches across large parts of Georgia and South Carolina—than Humberto did as a landfalling hurricane.
The research team, which was funded by the NOAA Climate Program Office’s Modeling, Analysis, Predictions and Projections (MAPP) program, the Department of Energy, and Stanford University, used rainfall measurements from land-based weather stations dating back to the beginning of the twentieth century. They categorized Atlantic hurricanes affecting the southeastern and eastern United States based on both their lifetime maximum intensity and their intensity while they were raining over land. The researchers found that, on average, rainfall was most extreme in situations like Irma; tropical storms evolved from major hurricanes dumped heavier precipitation over a wider area than other types of storms—even hurricanes or major hurricanes.
 The study should remind us of the limitations inherent in the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, which designates hurricanes by categories 1-5 based on their sustained wind speed. When we’re anticipating the destructive power of landfalling tropical cyclones, we miss half the picture if we focus only on high winds and discount extreme precipitation. Tropical storms may be officially designated as “weaker” than hurricanes, but their precipitation can be deadly.
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace Michaels
The study should remind us of the limitations inherent in the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, which designates hurricanes by categories 1-5 based on their sustained wind speed. When we’re anticipating the destructive power of landfalling tropical cyclones, we miss half the picture if we focus only on high winds and discount extreme precipitation. Tropical storms may be officially designated as “weaker” than hurricanes, but their precipitation can be deadly.
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace Michaels
 These rainfall maps offer an example of the somewhat counterintuitive pattern. The top map shows 24-hour total precipitation from former-Hurricane Irma on September 11, 2017, 12:00 UTC, when it was a tropical storm. The bottom map shows 24-hour rainfall totals from Hurricane Humberto on September 13, 2007, 12:00 UTC, while it was a hurricane. Darker colors indicate heavier precipitation. Irma as a tropical storm had a larger spatial extent and heavier rainfall—one-day totals were more than 5 inches across large parts of Georgia and South Carolina—than Humberto did as a landfalling hurricane.
The research team, which was funded by the NOAA Climate Program Office’s Modeling, Analysis, Predictions and Projections (MAPP) program, the Department of Energy, and Stanford University, used rainfall measurements from land-based weather stations dating back to the beginning of the twentieth century. They categorized Atlantic hurricanes affecting the southeastern and eastern United States based on both their lifetime maximum intensity and their intensity while they were raining over land. The researchers found that, on average, rainfall was most extreme in situations like Irma; tropical storms evolved from major hurricanes dumped heavier precipitation over a wider area than other types of storms—even hurricanes or major hurricanes.
These rainfall maps offer an example of the somewhat counterintuitive pattern. The top map shows 24-hour total precipitation from former-Hurricane Irma on September 11, 2017, 12:00 UTC, when it was a tropical storm. The bottom map shows 24-hour rainfall totals from Hurricane Humberto on September 13, 2007, 12:00 UTC, while it was a hurricane. Darker colors indicate heavier precipitation. Irma as a tropical storm had a larger spatial extent and heavier rainfall—one-day totals were more than 5 inches across large parts of Georgia and South Carolina—than Humberto did as a landfalling hurricane.
The research team, which was funded by the NOAA Climate Program Office’s Modeling, Analysis, Predictions and Projections (MAPP) program, the Department of Energy, and Stanford University, used rainfall measurements from land-based weather stations dating back to the beginning of the twentieth century. They categorized Atlantic hurricanes affecting the southeastern and eastern United States based on both their lifetime maximum intensity and their intensity while they were raining over land. The researchers found that, on average, rainfall was most extreme in situations like Irma; tropical storms evolved from major hurricanes dumped heavier precipitation over a wider area than other types of storms—even hurricanes or major hurricanes.
 The study should remind us of the limitations inherent in the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, which designates hurricanes by categories 1-5 based on their sustained wind speed. When we’re anticipating the destructive power of landfalling tropical cyclones, we miss half the picture if we focus only on high winds and discount extreme precipitation. Tropical storms may be officially designated as “weaker” than hurricanes, but their precipitation can be deadly.
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace Michaels
The study should remind us of the limitations inherent in the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, which designates hurricanes by categories 1-5 based on their sustained wind speed. When we’re anticipating the destructive power of landfalling tropical cyclones, we miss half the picture if we focus only on high winds and discount extreme precipitation. Tropical storms may be officially designated as “weaker” than hurricanes, but their precipitation can be deadly.
Edited for WeatherNation by Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More