Catastrophic Wildfires in Southeastern Australia
Special Stories
8 Jan 2020 1:30 AM
[A river of smoke from bushfires in Victoria and New South Wales, Australia, on January 2, 2020. NASA satellite image courtesy Worldview website.]
[NOAA by Rebecca Lindsey] Terrible wildfires raged through parts of southeastern Australia in the first days of 2020, and the news has been filled with stories of tragedy and destruction in communities in New South Wales and Victoria. Smoke shrouded the nation’s capital, Canberra, and spread out across the ocean as a yellow-brown river.
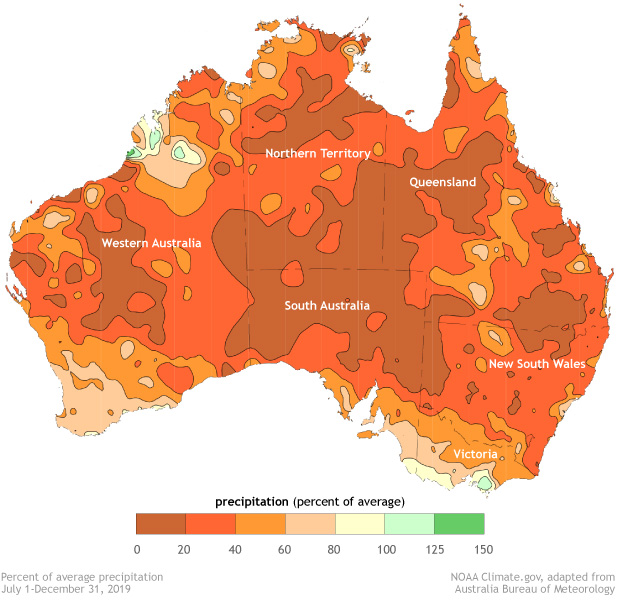
The devastating fire season, which began in Queensland in September and has progressed southward, is the result of an extremely dry and warm spring and early summer. According to the spring report from the Australia Bureau of Meteorology, it was the driest spring on record for the country as a whole, with rainfall below average almost everywhere. Meanwhile, the average daytime high temperature for spring was above or very much above average across nearly all of Australia.
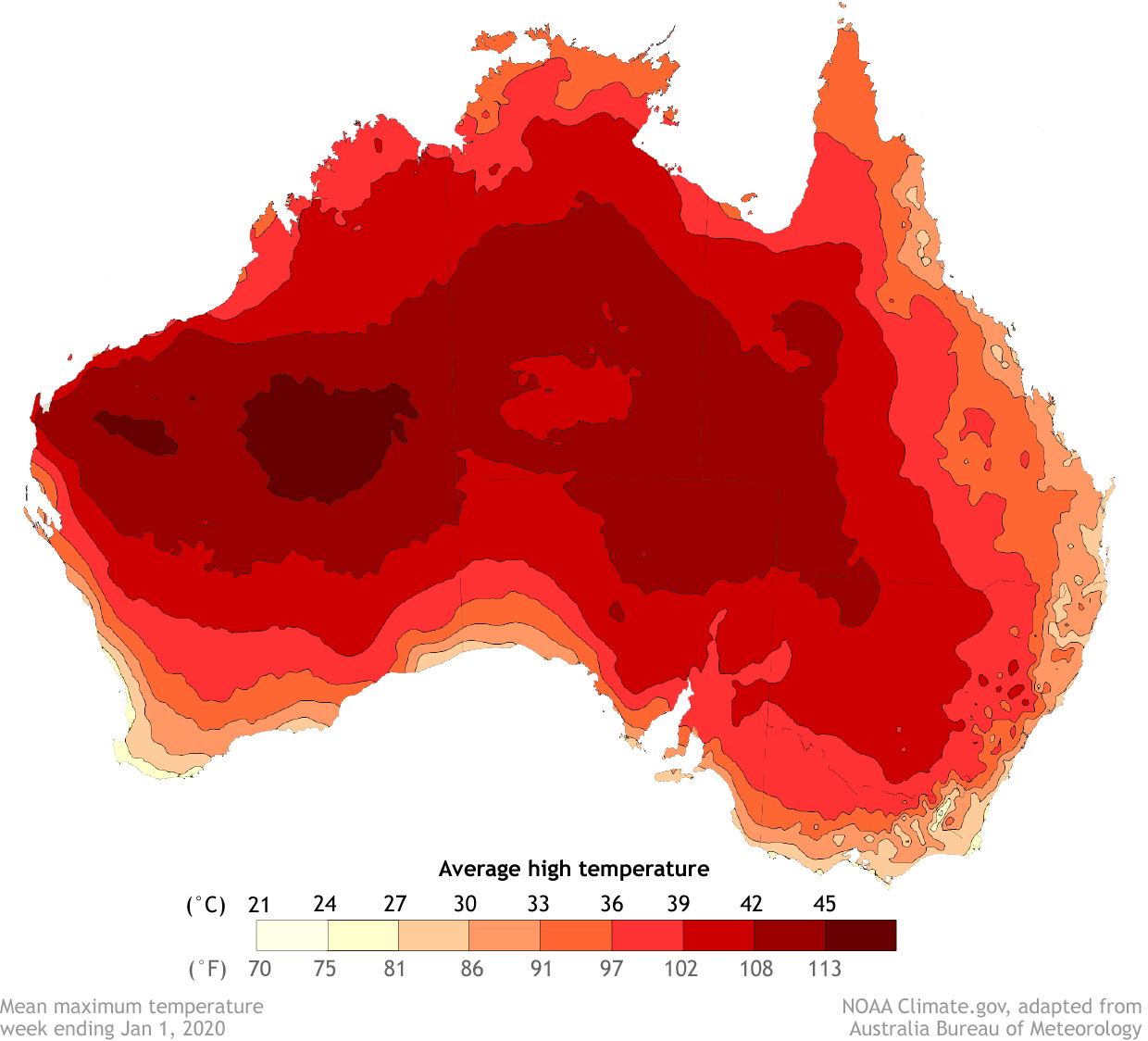
 As spring turned to summer, a scorching heatwave spread across the country. The national average maximum temperature was 105.6 degrees Fahrenheit (40.9 degrees Celsius) according to the New York Times, topping the previous record of 104.5 degrees F (40.3 degrees C) set in January 2013. The heat and dryness combined to push the spring Forest Fire Danger Index to record high levels across the entire country, according to a special weather statement issued by the Bureau of Meteorology on December 18, 2019. Extreme heat has continued into the new year.
As spring turned to summer, a scorching heatwave spread across the country. The national average maximum temperature was 105.6 degrees Fahrenheit (40.9 degrees Celsius) according to the New York Times, topping the previous record of 104.5 degrees F (40.3 degrees C) set in January 2013. The heat and dryness combined to push the spring Forest Fire Danger Index to record high levels across the entire country, according to a special weather statement issued by the Bureau of Meteorology on December 18, 2019. Extreme heat has continued into the new year.
 The number of cool days in Australia has declined, while the number of days with extremely warm daytime high temperatures has increased.
The number of cool days in Australia has declined, while the number of days with extremely warm daytime high temperatures has increased.
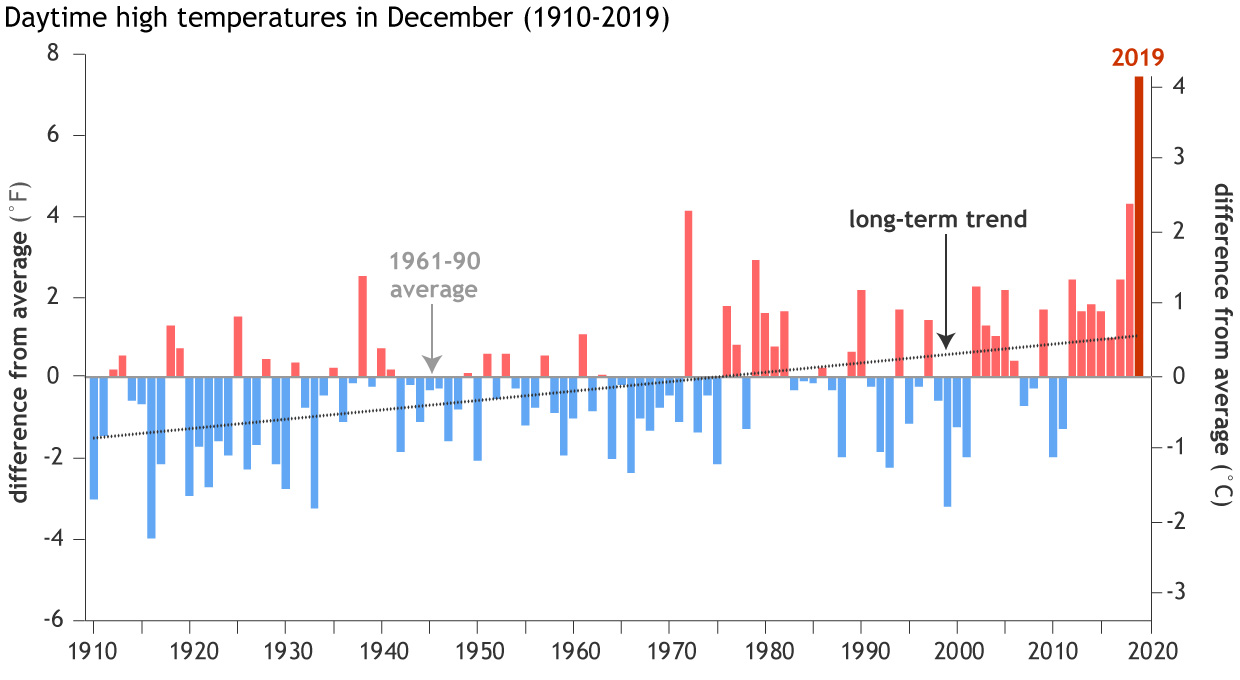 This increase in extremely hot days is contributing to observed trends in increasing forest fire danger across many parts of Australia over the past few decades, especially in the southeast during the Southern Hemisphere spring months of September-November. Just last month, in a special collection of extreme event analyses published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, experts concluded that rising temperatures contributed to the 2018 exceptional fire season in Queensland.
This increase in extremely hot days is contributing to observed trends in increasing forest fire danger across many parts of Australia over the past few decades, especially in the southeast during the Southern Hemisphere spring months of September-November. Just last month, in a special collection of extreme event analyses published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, experts concluded that rising temperatures contributed to the 2018 exceptional fire season in Queensland.

[Percent of average rainfall for the period July 1–December 31, 2019. NOAA Climate image adapted from original by Australian Bureau of Meteorology]

[Average daytime high temperature for the week ending January 1, 2010. NOAA Climate image adapted from original by Australian Bureau of Meteorology]

[December daytime high (maximum) temperatures from 1910–2019 compared to the 1961-1990 average. NOAA Climate data, based on data from Australia Bureau of Meteorology.]
All Weather News
More