Century Long Snowpack Study Shows Levels in Decline in Western States
Special Stories
6 Mar 2018 7:50 AM
From Oregon State University
A new study of long-term snow monitoring sites in the western United States found declines in snowpack at more than 90 percent of those sites – and one-third of the declines were deemed significant.
Since 1915, the average snowpack in western states has declined by between 15 and 30 percent, the researchers say, and the amount of water lost from that snowpack reduction is comparable in volume to Lake Mead, the West’s largest manmade reservoir. The loss of water storage can have an impact on municipal, industrial and agricultural usage, as well as fish and other animals.
“It is a bigger decline than we had expected,” said Philip Mote, director of the Oregon Climate Change Research Institute at Oregon State University and lead author on the study. “In many lower-elevation sites, what used to fall as snow is now rain. Upper elevations have not been affected nearly as much, but most states don’t have that much area at 7,000-plus feet.
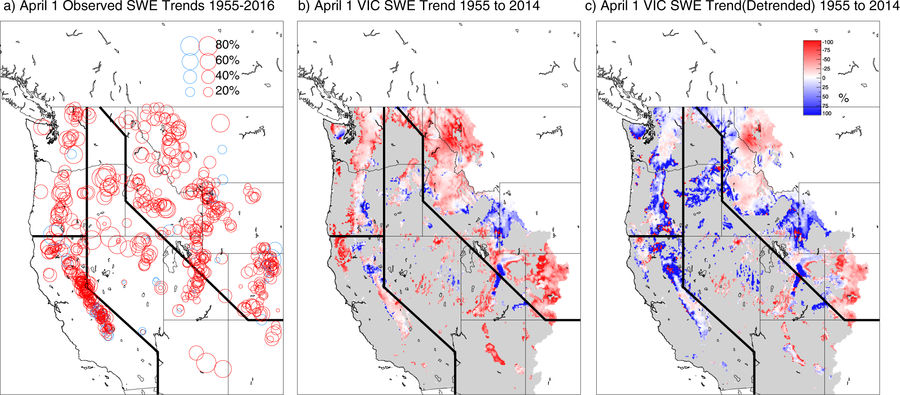 [Linear trends in 1 Apr SWE relative to the starting value for the linear fit (i.e., the 1955 value for the best-fit line): (a) at 699 snow course locations in the western United States for the period 1955–2016, with negative trends shown by red circles and positive by blue circles; (b) from the simulation using the VIC hydrologic model for the period 1955–2014 (cells in gray have mean April 1 SWE less than 5 mm; areas in white are not simulated); (c) as in (b) but using temperature data in which linear trends have been removed for the 1954-2014 period. Lines on the maps divide the West into four regions for analysis shown in subsequent figures]
“The solution isn’t in infrastructure. New reservoirs could not be built fast enough to offset the loss of snow storage – and we don’t have a lot of capacity left for that kind of storage. It comes down to managing what we have in the best possible ways.”
The consequences are significant, they point out. Earlier spring-like weather from warmer temperatures means more of the precipitation will not be stored as long in the mountains, which can result in lower river and reservoir levels during late summer and early fall.
The study considered data from 1,766 sites in the western U.S., mostly from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Natural Resources Conservation Service and the California Department of Water Resources. The researchers focused on measurements taken on April 1, which historically has been the high point for snowpack in most areas, though they also looked at measurements for Jan. 1, Feb. 1, March 1, and May 1 – which led to the range of decline of 15 to 30 percent.
They also used a physically based computer model of the hydrologic cycle, which takes daily weather observations and computes the snow accumulation, melting, and runoff to estimate the total snowpack in the western U.S.
[Linear trends in 1 Apr SWE relative to the starting value for the linear fit (i.e., the 1955 value for the best-fit line): (a) at 699 snow course locations in the western United States for the period 1955–2016, with negative trends shown by red circles and positive by blue circles; (b) from the simulation using the VIC hydrologic model for the period 1955–2014 (cells in gray have mean April 1 SWE less than 5 mm; areas in white are not simulated); (c) as in (b) but using temperature data in which linear trends have been removed for the 1954-2014 period. Lines on the maps divide the West into four regions for analysis shown in subsequent figures]
“The solution isn’t in infrastructure. New reservoirs could not be built fast enough to offset the loss of snow storage – and we don’t have a lot of capacity left for that kind of storage. It comes down to managing what we have in the best possible ways.”
The consequences are significant, they point out. Earlier spring-like weather from warmer temperatures means more of the precipitation will not be stored as long in the mountains, which can result in lower river and reservoir levels during late summer and early fall.
The study considered data from 1,766 sites in the western U.S., mostly from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Natural Resources Conservation Service and the California Department of Water Resources. The researchers focused on measurements taken on April 1, which historically has been the high point for snowpack in most areas, though they also looked at measurements for Jan. 1, Feb. 1, March 1, and May 1 – which led to the range of decline of 15 to 30 percent.
They also used a physically based computer model of the hydrologic cycle, which takes daily weather observations and computes the snow accumulation, melting, and runoff to estimate the total snowpack in the western U.S.
 [2015 in Oregon had low snowpacks and less water in many lakes and rivers. Pictured is Wallowa Lake in northeastern Oregon. Credit: Oregon State University]
“We found declining trends in all months, states and climates,” Mote said, “but the impacts are the largest in the spring, in Pacific states, and in locations with mild winter climates.”
The Pacific states – California, Oregon and Washington – receive more precipitation because of the Pacific Ocean influence, and more of the snow falls at temperatures near freezing. Because the Cascade Mountains, which transect the region, are not as steep as the Rocky Mountains, they have more area that is affected by changes in temperature.
“When you raise the snow zone level 300 feet, it covers a much broader swath than it would in the inland states,” Mote said.
Mote was one of 12 lead authors on a chapter of the fifth Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report looking at the cryosphere, which is comprised of snow, river and lake ice, sea ice, glaciers, ice sheets and frozen ground. Also an author on the fourth IPCC report, he had led a 2005 study on western snowpack levels that had also documented declines that were less dramatic than those in this new study.
This latest study found:
[2015 in Oregon had low snowpacks and less water in many lakes and rivers. Pictured is Wallowa Lake in northeastern Oregon. Credit: Oregon State University]
“We found declining trends in all months, states and climates,” Mote said, “but the impacts are the largest in the spring, in Pacific states, and in locations with mild winter climates.”
The Pacific states – California, Oregon and Washington – receive more precipitation because of the Pacific Ocean influence, and more of the snow falls at temperatures near freezing. Because the Cascade Mountains, which transect the region, are not as steep as the Rocky Mountains, they have more area that is affected by changes in temperature.
“When you raise the snow zone level 300 feet, it covers a much broader swath than it would in the inland states,” Mote said.
Mote was one of 12 lead authors on a chapter of the fifth Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report looking at the cryosphere, which is comprised of snow, river and lake ice, sea ice, glaciers, ice sheets and frozen ground. Also an author on the fourth IPCC report, he had led a 2005 study on western snowpack levels that had also documented declines that were less dramatic than those in this new study.
This latest study found:
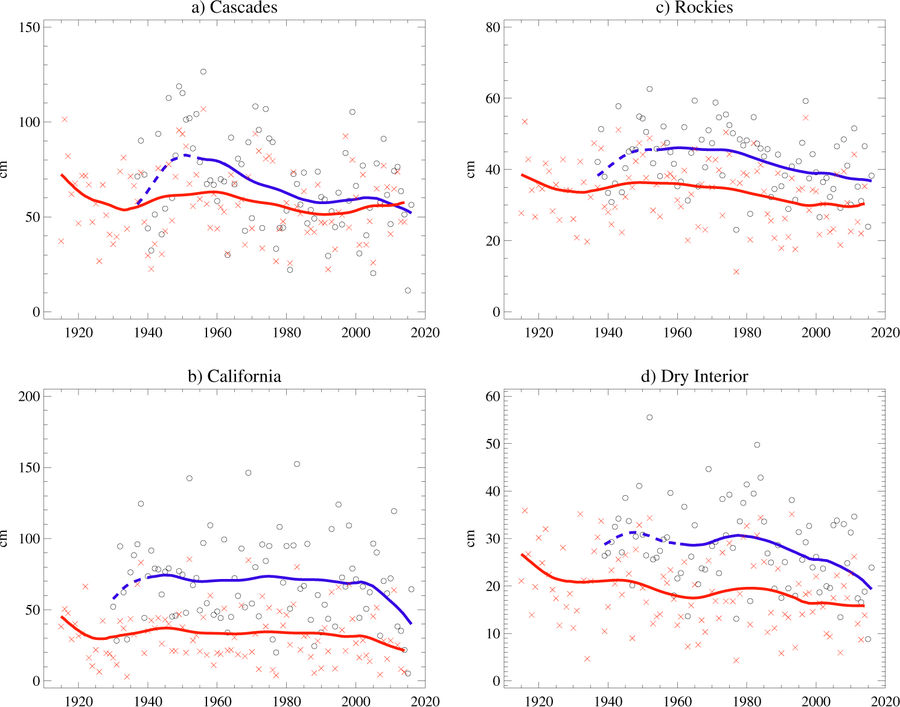 [Time series of regional mean 1 Apr SWE for the domains indicated in Fig. 1, for observations (black circles) and VIC (red crosses). Smooth curves are added for VIC (red) and for the period of observations when at least a quarter (blue dashed) or half (blue solid) the locations were reporting. In computing regional averages for VIC, only grid cells with mean 1 April SWE > 50 mm are included]
“The amount of water in the snowpack of the western United States is roughly equivalent to all of the stored water in the largest reservoirs of those states,” Mote said. “We’ve pretty much spent a century building up those water supplies at the same time the natural supply of snowpack is dwindling.
“On smaller reservoirs, the water supply can be replenished after one bad year. But a reservoir like Lake Mead takes four years of normal flows to fill; it still hasn’t recovered from the drought of the early 2000s.”
Mote said snowpack levels in most of the western U.S. for 2017-18 thus far are lower than average – a function of continued warming temperatures and the presence of a La Niña event, which typically results in warmer and drier conditions in most southwestern states.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
[Time series of regional mean 1 Apr SWE for the domains indicated in Fig. 1, for observations (black circles) and VIC (red crosses). Smooth curves are added for VIC (red) and for the period of observations when at least a quarter (blue dashed) or half (blue solid) the locations were reporting. In computing regional averages for VIC, only grid cells with mean 1 April SWE > 50 mm are included]
“The amount of water in the snowpack of the western United States is roughly equivalent to all of the stored water in the largest reservoirs of those states,” Mote said. “We’ve pretty much spent a century building up those water supplies at the same time the natural supply of snowpack is dwindling.
“On smaller reservoirs, the water supply can be replenished after one bad year. But a reservoir like Lake Mead takes four years of normal flows to fill; it still hasn’t recovered from the drought of the early 2000s.”
Mote said snowpack levels in most of the western U.S. for 2017-18 thus far are lower than average – a function of continued warming temperatures and the presence of a La Niña event, which typically results in warmer and drier conditions in most southwestern states.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
 [Linear trends in 1 Apr SWE relative to the starting value for the linear fit (i.e., the 1955 value for the best-fit line): (a) at 699 snow course locations in the western United States for the period 1955–2016, with negative trends shown by red circles and positive by blue circles; (b) from the simulation using the VIC hydrologic model for the period 1955–2014 (cells in gray have mean April 1 SWE less than 5 mm; areas in white are not simulated); (c) as in (b) but using temperature data in which linear trends have been removed for the 1954-2014 period. Lines on the maps divide the West into four regions for analysis shown in subsequent figures]
“The solution isn’t in infrastructure. New reservoirs could not be built fast enough to offset the loss of snow storage – and we don’t have a lot of capacity left for that kind of storage. It comes down to managing what we have in the best possible ways.”
The consequences are significant, they point out. Earlier spring-like weather from warmer temperatures means more of the precipitation will not be stored as long in the mountains, which can result in lower river and reservoir levels during late summer and early fall.
The study considered data from 1,766 sites in the western U.S., mostly from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Natural Resources Conservation Service and the California Department of Water Resources. The researchers focused on measurements taken on April 1, which historically has been the high point for snowpack in most areas, though they also looked at measurements for Jan. 1, Feb. 1, March 1, and May 1 – which led to the range of decline of 15 to 30 percent.
They also used a physically based computer model of the hydrologic cycle, which takes daily weather observations and computes the snow accumulation, melting, and runoff to estimate the total snowpack in the western U.S.
[Linear trends in 1 Apr SWE relative to the starting value for the linear fit (i.e., the 1955 value for the best-fit line): (a) at 699 snow course locations in the western United States for the period 1955–2016, with negative trends shown by red circles and positive by blue circles; (b) from the simulation using the VIC hydrologic model for the period 1955–2014 (cells in gray have mean April 1 SWE less than 5 mm; areas in white are not simulated); (c) as in (b) but using temperature data in which linear trends have been removed for the 1954-2014 period. Lines on the maps divide the West into four regions for analysis shown in subsequent figures]
“The solution isn’t in infrastructure. New reservoirs could not be built fast enough to offset the loss of snow storage – and we don’t have a lot of capacity left for that kind of storage. It comes down to managing what we have in the best possible ways.”
The consequences are significant, they point out. Earlier spring-like weather from warmer temperatures means more of the precipitation will not be stored as long in the mountains, which can result in lower river and reservoir levels during late summer and early fall.
The study considered data from 1,766 sites in the western U.S., mostly from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Natural Resources Conservation Service and the California Department of Water Resources. The researchers focused on measurements taken on April 1, which historically has been the high point for snowpack in most areas, though they also looked at measurements for Jan. 1, Feb. 1, March 1, and May 1 – which led to the range of decline of 15 to 30 percent.
They also used a physically based computer model of the hydrologic cycle, which takes daily weather observations and computes the snow accumulation, melting, and runoff to estimate the total snowpack in the western U.S.
 [2015 in Oregon had low snowpacks and less water in many lakes and rivers. Pictured is Wallowa Lake in northeastern Oregon. Credit: Oregon State University]
“We found declining trends in all months, states and climates,” Mote said, “but the impacts are the largest in the spring, in Pacific states, and in locations with mild winter climates.”
The Pacific states – California, Oregon and Washington – receive more precipitation because of the Pacific Ocean influence, and more of the snow falls at temperatures near freezing. Because the Cascade Mountains, which transect the region, are not as steep as the Rocky Mountains, they have more area that is affected by changes in temperature.
“When you raise the snow zone level 300 feet, it covers a much broader swath than it would in the inland states,” Mote said.
Mote was one of 12 lead authors on a chapter of the fifth Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report looking at the cryosphere, which is comprised of snow, river and lake ice, sea ice, glaciers, ice sheets and frozen ground. Also an author on the fourth IPCC report, he had led a 2005 study on western snowpack levels that had also documented declines that were less dramatic than those in this new study.
This latest study found:
[2015 in Oregon had low snowpacks and less water in many lakes and rivers. Pictured is Wallowa Lake in northeastern Oregon. Credit: Oregon State University]
“We found declining trends in all months, states and climates,” Mote said, “but the impacts are the largest in the spring, in Pacific states, and in locations with mild winter climates.”
The Pacific states – California, Oregon and Washington – receive more precipitation because of the Pacific Ocean influence, and more of the snow falls at temperatures near freezing. Because the Cascade Mountains, which transect the region, are not as steep as the Rocky Mountains, they have more area that is affected by changes in temperature.
“When you raise the snow zone level 300 feet, it covers a much broader swath than it would in the inland states,” Mote said.
Mote was one of 12 lead authors on a chapter of the fifth Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report looking at the cryosphere, which is comprised of snow, river and lake ice, sea ice, glaciers, ice sheets and frozen ground. Also an author on the fourth IPCC report, he had led a 2005 study on western snowpack levels that had also documented declines that were less dramatic than those in this new study.
This latest study found:
- California had the highest number of positive snowpack trends since 1955, but lingering drought during the past decade erased most of those gains and snowpack declines still dominated;
- Most of the other western states had only one or two sites that reported increases in snowpack;
- Regions with the most significant decrease in snowpack were eastern Oregon and northern Nevada, though snowpack decreases in excess of 70 percent also occurred in California, Montana, Washington, Idaho and Arizona.
 [Time series of regional mean 1 Apr SWE for the domains indicated in Fig. 1, for observations (black circles) and VIC (red crosses). Smooth curves are added for VIC (red) and for the period of observations when at least a quarter (blue dashed) or half (blue solid) the locations were reporting. In computing regional averages for VIC, only grid cells with mean 1 April SWE > 50 mm are included]
“The amount of water in the snowpack of the western United States is roughly equivalent to all of the stored water in the largest reservoirs of those states,” Mote said. “We’ve pretty much spent a century building up those water supplies at the same time the natural supply of snowpack is dwindling.
“On smaller reservoirs, the water supply can be replenished after one bad year. But a reservoir like Lake Mead takes four years of normal flows to fill; it still hasn’t recovered from the drought of the early 2000s.”
Mote said snowpack levels in most of the western U.S. for 2017-18 thus far are lower than average – a function of continued warming temperatures and the presence of a La Niña event, which typically results in warmer and drier conditions in most southwestern states.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
[Time series of regional mean 1 Apr SWE for the domains indicated in Fig. 1, for observations (black circles) and VIC (red crosses). Smooth curves are added for VIC (red) and for the period of observations when at least a quarter (blue dashed) or half (blue solid) the locations were reporting. In computing regional averages for VIC, only grid cells with mean 1 April SWE > 50 mm are included]
“The amount of water in the snowpack of the western United States is roughly equivalent to all of the stored water in the largest reservoirs of those states,” Mote said. “We’ve pretty much spent a century building up those water supplies at the same time the natural supply of snowpack is dwindling.
“On smaller reservoirs, the water supply can be replenished after one bad year. But a reservoir like Lake Mead takes four years of normal flows to fill; it still hasn’t recovered from the drought of the early 2000s.”
Mote said snowpack levels in most of the western U.S. for 2017-18 thus far are lower than average – a function of continued warming temperatures and the presence of a La Niña event, which typically results in warmer and drier conditions in most southwestern states.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More