GOES-17 Releases ‘First Light’ Imagery from its Advanced Baseline Imager
Special Stories
1 Jun 2018 10:38 AM
From NOAA
The first imagery from NOAA’s GOES-17 Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) made its public debut yesterday (May 31st). While experts continue to address an issue with the cooling system of the satellite’s imager, new views from GOES-17 show that its ABI is providing beautiful – and useful – imagery of the Western Hemisphere. This imagery was created using two visible bands (blue and red) and one near-infrared “vegetation” band that are functional with the current cooling system performance.
The imagery also incorporates input from one of the ABI’s “longwave” infrared bands that is functional during a portion of the day despite the cooling system issue.
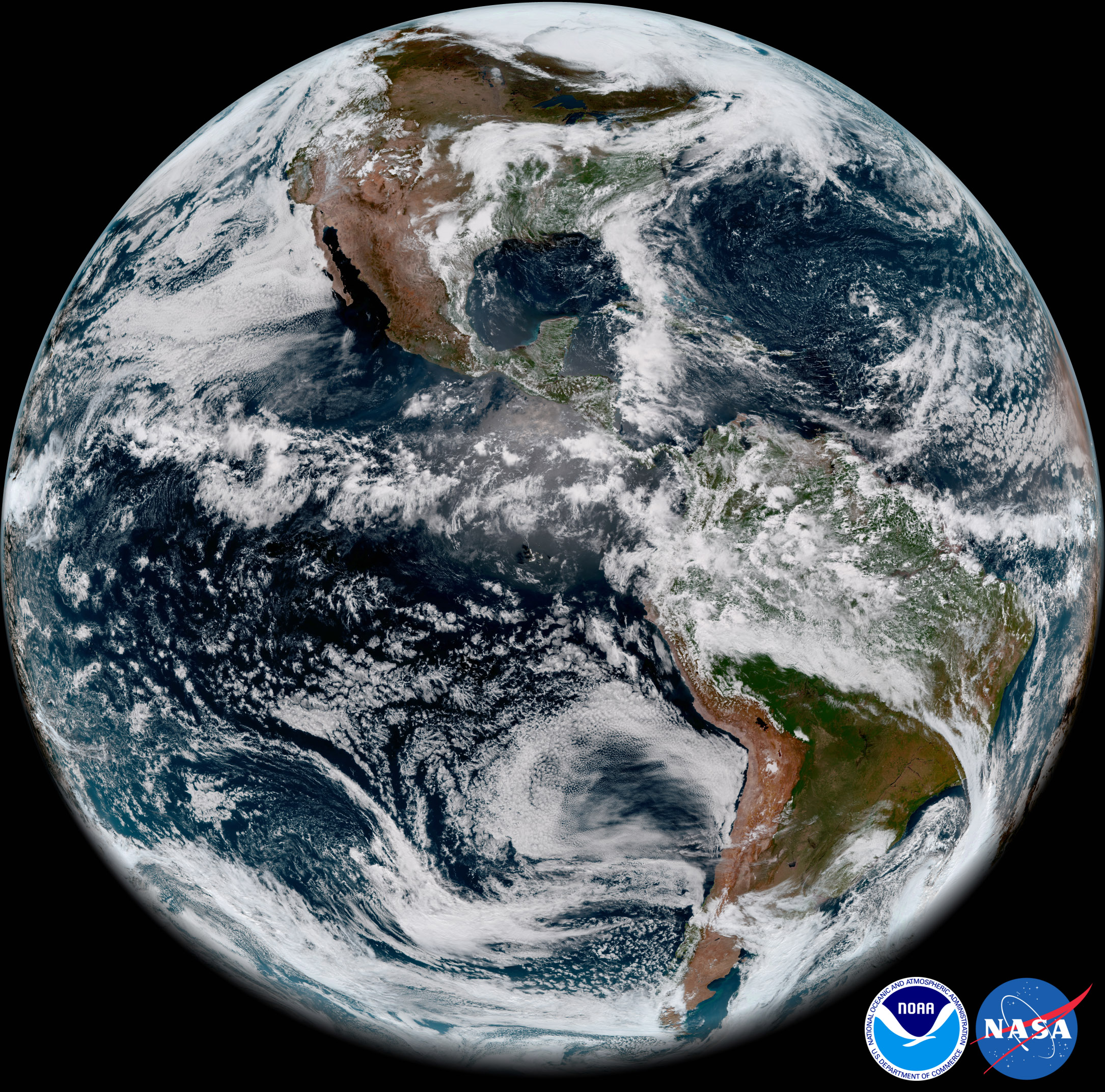 [GOES-17 took this stunning, full-disk snapshot of Earth’s Western Hemisphere from its checkout position at 12:00 p.m. EDT on May 20, 2018, using the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) instrument. GOES-17 observes Earth from an equatorial vantage point approximately 22,300 miles above the surface. Credit: NOAA/NASA]
When combined as a “GeoColor” image, depicting the Earth in vivid detail and colors intuitive to human vision, these bands provide valuable information for monitoring dust, haze, smoke, clouds, fog, winds and vegetation. ABI imagery also provides information on cloud motion, helping meteorologists monitor and forecast severe weather and hurricanes. The improved resolution and faster scanning ability of the instrument compared to the previous generation of GOES allow forecasters to more rapidly detect and analyze storms as they are developing and intensifying.
GOES-17 is the second in a series of next-generation geostationary weather satellites. Like GOES-16, its sister satellite operating as GOES East, GOES-17 is designed to provide advanced imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth from 22,300 miles above the equator.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7XlfE0ndv_g
GOES-17 launched on March 1, 2018, from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The satellite is currently in its post-launch checkout and testing phase, the period in which its instruments and systems are calibrated, validated and assessed for operational usage. Imagery released from GOES-17 during the post-launch testing phase should be considered preliminary and non-operational.
NOAA’s operational geostationary constellation - GOES-16, operating as GOES-East, GOES-15, operating as GOES-West and GOES-14, operating as the on-orbit spare - is healthy and monitoring weather across the nation each day.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
[GOES-17 took this stunning, full-disk snapshot of Earth’s Western Hemisphere from its checkout position at 12:00 p.m. EDT on May 20, 2018, using the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) instrument. GOES-17 observes Earth from an equatorial vantage point approximately 22,300 miles above the surface. Credit: NOAA/NASA]
When combined as a “GeoColor” image, depicting the Earth in vivid detail and colors intuitive to human vision, these bands provide valuable information for monitoring dust, haze, smoke, clouds, fog, winds and vegetation. ABI imagery also provides information on cloud motion, helping meteorologists monitor and forecast severe weather and hurricanes. The improved resolution and faster scanning ability of the instrument compared to the previous generation of GOES allow forecasters to more rapidly detect and analyze storms as they are developing and intensifying.
GOES-17 is the second in a series of next-generation geostationary weather satellites. Like GOES-16, its sister satellite operating as GOES East, GOES-17 is designed to provide advanced imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth from 22,300 miles above the equator.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7XlfE0ndv_g
GOES-17 launched on March 1, 2018, from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The satellite is currently in its post-launch checkout and testing phase, the period in which its instruments and systems are calibrated, validated and assessed for operational usage. Imagery released from GOES-17 during the post-launch testing phase should be considered preliminary and non-operational.
NOAA’s operational geostationary constellation - GOES-16, operating as GOES-East, GOES-15, operating as GOES-West and GOES-14, operating as the on-orbit spare - is healthy and monitoring weather across the nation each day.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
 [GOES-17 took this stunning, full-disk snapshot of Earth’s Western Hemisphere from its checkout position at 12:00 p.m. EDT on May 20, 2018, using the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) instrument. GOES-17 observes Earth from an equatorial vantage point approximately 22,300 miles above the surface. Credit: NOAA/NASA]
When combined as a “GeoColor” image, depicting the Earth in vivid detail and colors intuitive to human vision, these bands provide valuable information for monitoring dust, haze, smoke, clouds, fog, winds and vegetation. ABI imagery also provides information on cloud motion, helping meteorologists monitor and forecast severe weather and hurricanes. The improved resolution and faster scanning ability of the instrument compared to the previous generation of GOES allow forecasters to more rapidly detect and analyze storms as they are developing and intensifying.
GOES-17 is the second in a series of next-generation geostationary weather satellites. Like GOES-16, its sister satellite operating as GOES East, GOES-17 is designed to provide advanced imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth from 22,300 miles above the equator.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7XlfE0ndv_g
GOES-17 launched on March 1, 2018, from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The satellite is currently in its post-launch checkout and testing phase, the period in which its instruments and systems are calibrated, validated and assessed for operational usage. Imagery released from GOES-17 during the post-launch testing phase should be considered preliminary and non-operational.
NOAA’s operational geostationary constellation - GOES-16, operating as GOES-East, GOES-15, operating as GOES-West and GOES-14, operating as the on-orbit spare - is healthy and monitoring weather across the nation each day.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
[GOES-17 took this stunning, full-disk snapshot of Earth’s Western Hemisphere from its checkout position at 12:00 p.m. EDT on May 20, 2018, using the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) instrument. GOES-17 observes Earth from an equatorial vantage point approximately 22,300 miles above the surface. Credit: NOAA/NASA]
When combined as a “GeoColor” image, depicting the Earth in vivid detail and colors intuitive to human vision, these bands provide valuable information for monitoring dust, haze, smoke, clouds, fog, winds and vegetation. ABI imagery also provides information on cloud motion, helping meteorologists monitor and forecast severe weather and hurricanes. The improved resolution and faster scanning ability of the instrument compared to the previous generation of GOES allow forecasters to more rapidly detect and analyze storms as they are developing and intensifying.
GOES-17 is the second in a series of next-generation geostationary weather satellites. Like GOES-16, its sister satellite operating as GOES East, GOES-17 is designed to provide advanced imagery and atmospheric measurements of Earth from 22,300 miles above the equator.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7XlfE0ndv_g
GOES-17 launched on March 1, 2018, from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The satellite is currently in its post-launch checkout and testing phase, the period in which its instruments and systems are calibrated, validated and assessed for operational usage. Imagery released from GOES-17 during the post-launch testing phase should be considered preliminary and non-operational.
NOAA’s operational geostationary constellation - GOES-16, operating as GOES-East, GOES-15, operating as GOES-West and GOES-14, operating as the on-orbit spare - is healthy and monitoring weather across the nation each day.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More