Researchers Evaluating Data from Hurricane Dorian to Improve Future Forecasts
Special Stories
15 Sep 2019 3:16 PM
[A truck with roof mounted instruments, called a mobile mesonet, recorded observations of Hurricane Dorian. Credit: Sean Waugh/ NOAA NSSL]
[NOAA] A team of scientists from NOAA and the University of Oklahoma were in Florida during Hurricane Dorian to collect weather data. The goal of the research team, led by Michael Biggerstaff from OU and Sean Waugh from NOAA’s National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL), is to improve forecasts of damaging winds and deadly storm surge associated with hurricanes in addition to developing wind maps to inform new building codes.
“We want to help mitigate property damage by working with engineers and using our data to improve the building and construction codes needed to develop a more resilient national infrastructure in the future,” said Biggerstaff.
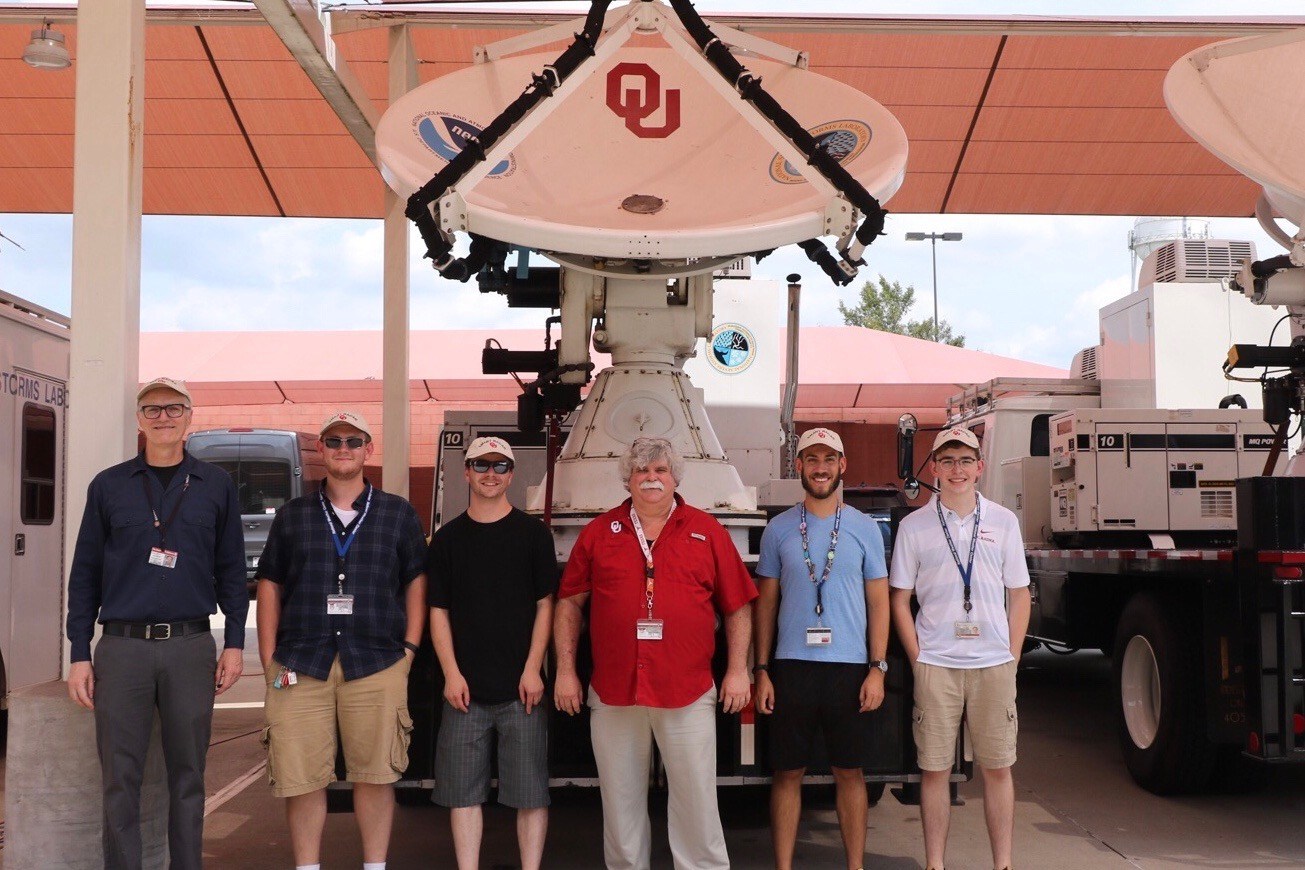 [University of Oklahoma meteorology team deployed during Hurricane Dorian. Image from OU]
The researchers used mobile weather radars and a Mobile Mesonet — a truck with weather instruments attached that will take wind measurements and launch weather balloons — to collect data. The mobile radars are able to produce high resolution wind maps over a 60-by-60 square mile area during hurricane landfalls.
The scientists hope the data will help them determine why hurricane winds can be so damaging, particularly to buildings and other structures. Wind gusts, duration of extreme winds, the amount of water entering a building from the storm, and changes in wind direction all impact building damage. Different parts of the hurricane create greater gust factors than other parts, so the ability to understand all of the components of the hurricane will aid in the development of cost-effective building codes to mitigate future damage.
[University of Oklahoma meteorology team deployed during Hurricane Dorian. Image from OU]
The researchers used mobile weather radars and a Mobile Mesonet — a truck with weather instruments attached that will take wind measurements and launch weather balloons — to collect data. The mobile radars are able to produce high resolution wind maps over a 60-by-60 square mile area during hurricane landfalls.
The scientists hope the data will help them determine why hurricane winds can be so damaging, particularly to buildings and other structures. Wind gusts, duration of extreme winds, the amount of water entering a building from the storm, and changes in wind direction all impact building damage. Different parts of the hurricane create greater gust factors than other parts, so the ability to understand all of the components of the hurricane will aid in the development of cost-effective building codes to mitigate future damage.
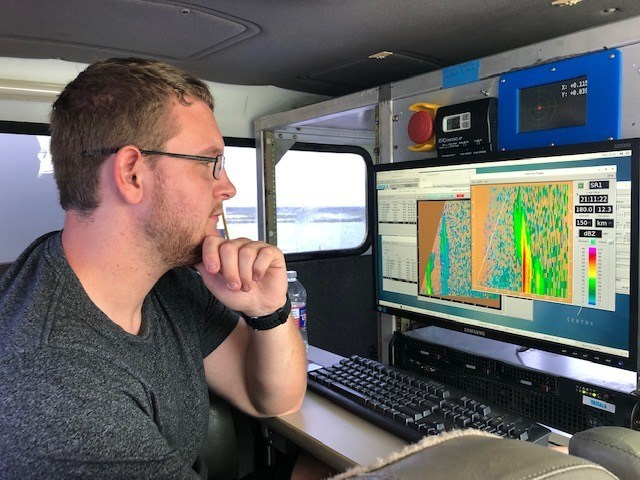 [Alec Prosser from the University of Oklahoma collecting data during Dorian in Florida. Image from OU]
In addition to this meteorological data, NOAA collected data on ocean conditions during Hurricane Dorian. Gliders released into the Atlantic Ocean earlier this summer were in the path of the storm, and even now are continuously collecting data on ocean temperature and salt content — factors that contribute to the intensity of hurricanes. Researchers aboard NOAA’s Hurricane Hunter aircraft also collected data that was fed into forecast models as well as used for research to improve these models.
[Alec Prosser from the University of Oklahoma collecting data during Dorian in Florida. Image from OU]
In addition to this meteorological data, NOAA collected data on ocean conditions during Hurricane Dorian. Gliders released into the Atlantic Ocean earlier this summer were in the path of the storm, and even now are continuously collecting data on ocean temperature and salt content — factors that contribute to the intensity of hurricanes. Researchers aboard NOAA’s Hurricane Hunter aircraft also collected data that was fed into forecast models as well as used for research to improve these models.
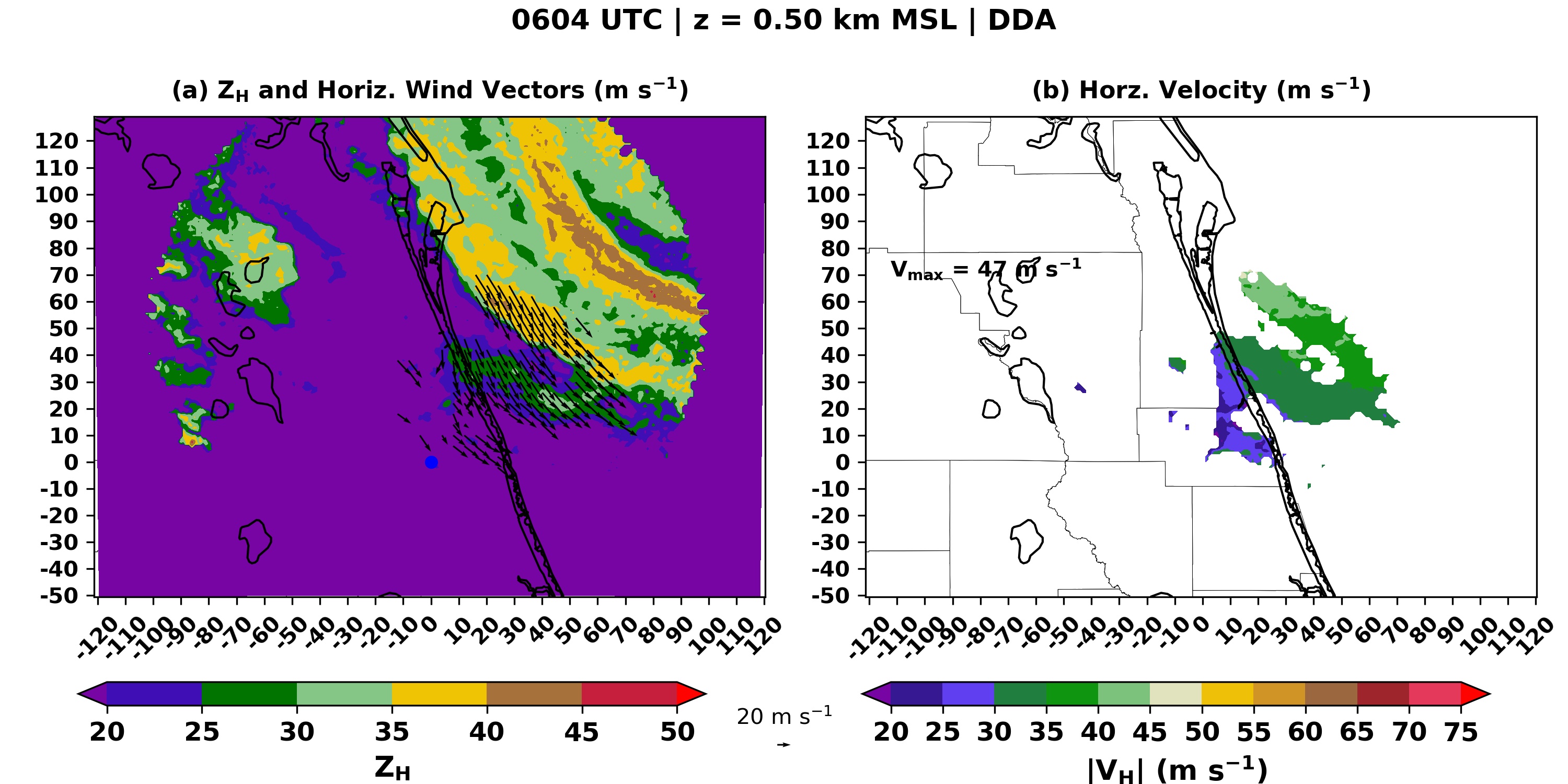
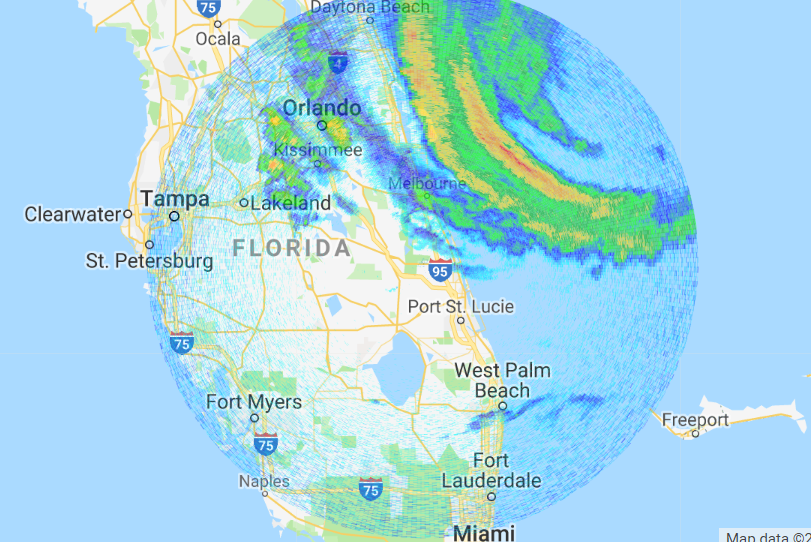 [Images from some of the Doppler radar data collected during Hurricane Dorian from University of Oklahoma]
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
[Images from some of the Doppler radar data collected during Hurricane Dorian from University of Oklahoma]
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
 [University of Oklahoma meteorology team deployed during Hurricane Dorian. Image from OU]
The researchers used mobile weather radars and a Mobile Mesonet — a truck with weather instruments attached that will take wind measurements and launch weather balloons — to collect data. The mobile radars are able to produce high resolution wind maps over a 60-by-60 square mile area during hurricane landfalls.
The scientists hope the data will help them determine why hurricane winds can be so damaging, particularly to buildings and other structures. Wind gusts, duration of extreme winds, the amount of water entering a building from the storm, and changes in wind direction all impact building damage. Different parts of the hurricane create greater gust factors than other parts, so the ability to understand all of the components of the hurricane will aid in the development of cost-effective building codes to mitigate future damage.
[University of Oklahoma meteorology team deployed during Hurricane Dorian. Image from OU]
The researchers used mobile weather radars and a Mobile Mesonet — a truck with weather instruments attached that will take wind measurements and launch weather balloons — to collect data. The mobile radars are able to produce high resolution wind maps over a 60-by-60 square mile area during hurricane landfalls.
The scientists hope the data will help them determine why hurricane winds can be so damaging, particularly to buildings and other structures. Wind gusts, duration of extreme winds, the amount of water entering a building from the storm, and changes in wind direction all impact building damage. Different parts of the hurricane create greater gust factors than other parts, so the ability to understand all of the components of the hurricane will aid in the development of cost-effective building codes to mitigate future damage.
 [Alec Prosser from the University of Oklahoma collecting data during Dorian in Florida. Image from OU]
In addition to this meteorological data, NOAA collected data on ocean conditions during Hurricane Dorian. Gliders released into the Atlantic Ocean earlier this summer were in the path of the storm, and even now are continuously collecting data on ocean temperature and salt content — factors that contribute to the intensity of hurricanes. Researchers aboard NOAA’s Hurricane Hunter aircraft also collected data that was fed into forecast models as well as used for research to improve these models.
[Alec Prosser from the University of Oklahoma collecting data during Dorian in Florida. Image from OU]
In addition to this meteorological data, NOAA collected data on ocean conditions during Hurricane Dorian. Gliders released into the Atlantic Ocean earlier this summer were in the path of the storm, and even now are continuously collecting data on ocean temperature and salt content — factors that contribute to the intensity of hurricanes. Researchers aboard NOAA’s Hurricane Hunter aircraft also collected data that was fed into forecast models as well as used for research to improve these models.

 [Images from some of the Doppler radar data collected during Hurricane Dorian from University of Oklahoma]
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
[Images from some of the Doppler radar data collected during Hurricane Dorian from University of Oklahoma]
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More