Spring Flood Outlook has Another Year of Widespread Flooding
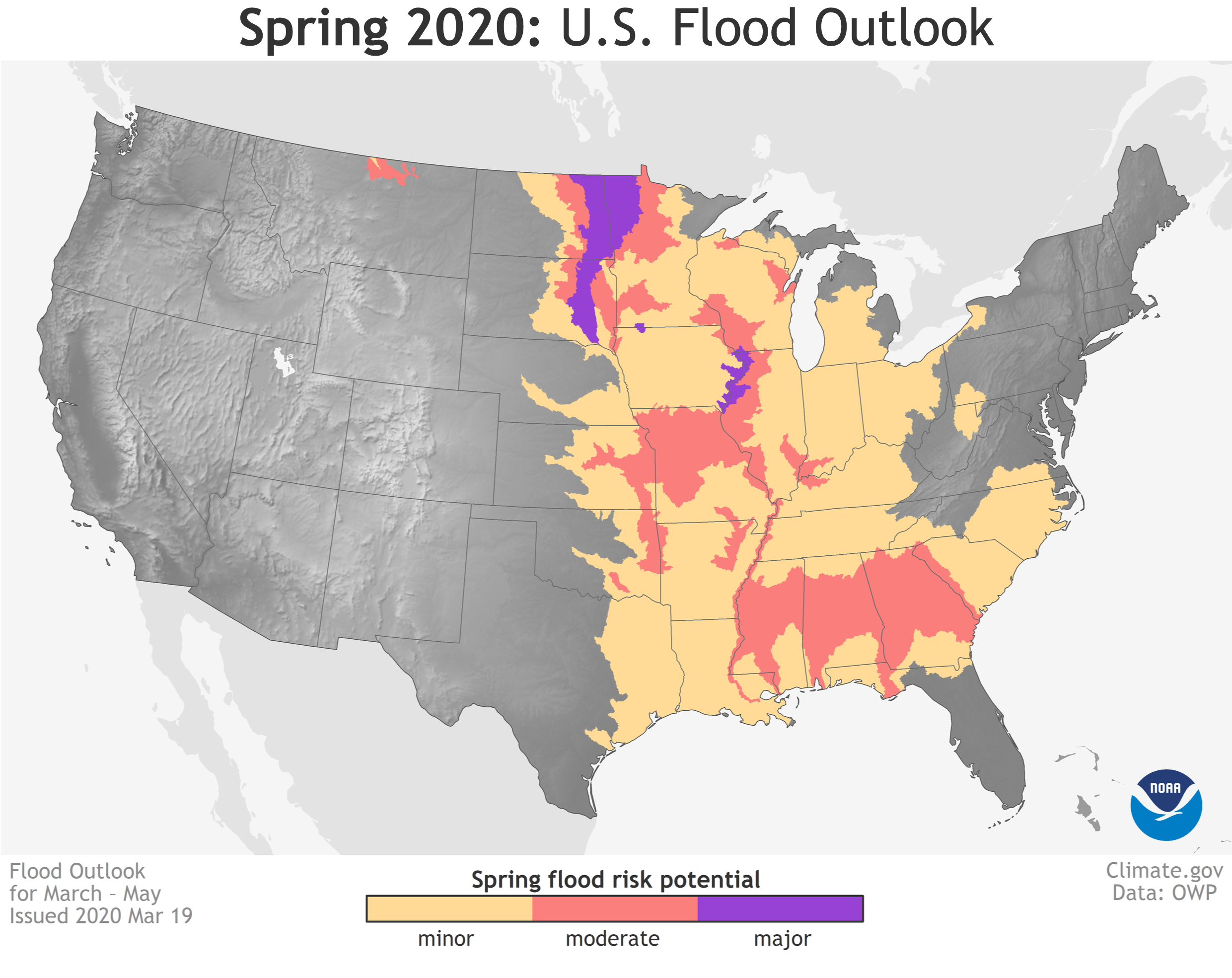
Ongoing rainfall, highly-saturated soil and an enhanced likelihood for above-normal precipitation this spring contribute to the increased chances for flooding across the central and southeastern United States. A risk of minor flooding exists across one-third of the country.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r-upsPTaZEA&feature=emb_logoThe greatest risk for major and moderate flood conditions includes the upper and middle Mississippi River basins, the Missouri River basin and the Red River of the North. Moderate flooding is anticipated in the Ohio, Cumberland, Tennessee, and Missouri River basins, as well as the lower Mississippi River basin and its tributaries.
“Nearly every day, dangerous flooding occurs somewhere in the United States and widespread flooding is in the forecast for many states in the months ahead,” said Ed Clark, director of NOAA’s National Water Center in Tuscaloosa, Alabama. “Working with our partners across the National Weather Service we provide the best available forecast products to enhance resilience in communities at greatest risk.”

With soil moisture already at high levels across much of the central U.S., and many rivers running high in the central and eastern U.S., any heavy local rainfall could trigger flooding in these high-risk areas. The flood risk outlook is based on an integrated evaluation of a number of factors, including current conditions of snowpack, drought, soil moisture, frost depth, streamflow and precipitation.
“People depend on the National Weather Service’s river forecasts, and the accurate and timely streamflow data from more than 8,400 streamgages operated by the U.S. Geological Survey throughout the country play an integral part in making those forecasts,” said Bob Holmes, Jr., Ph.D, USGS National Flood Coordinator. "These streamgages report information like when streams have reached flood stage or even when they break streamflow records. That kind of data allows the National Weather Service to bring the best science to bear for their forecasts."