The Day Spearfish, South Dakota Set a World Record
Special Stories
22 Jan 2018 5:55 PM
It was 75 years ago January 22, 1943 when Spearfish, SD. set and still holds the record for fastest temperature change.
 That day started out very cold in Spearfish, and at 7:30 am MST the temperature recorded was -4°F.
At that time Chinook winds picked up speed and two minutes later at 7:32 am the temperature rose to +45° F. This was a 49° increase in just two minutes that is a record that still stands.
Temperatures continued to rise and at 9:00 am the temperature reached +54° F. As the chinook winds died down and 27 minutes later the temperature dropped 58° F back to -4° F.
The rapid temperature fluctuation that day caused glass windows to crack and instantly frosted car windows.
That day started out very cold in Spearfish, and at 7:30 am MST the temperature recorded was -4°F.
At that time Chinook winds picked up speed and two minutes later at 7:32 am the temperature rose to +45° F. This was a 49° increase in just two minutes that is a record that still stands.
Temperatures continued to rise and at 9:00 am the temperature reached +54° F. As the chinook winds died down and 27 minutes later the temperature dropped 58° F back to -4° F.
The rapid temperature fluctuation that day caused glass windows to crack and instantly frosted car windows.
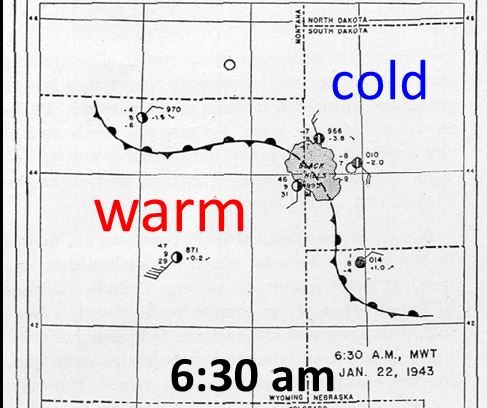
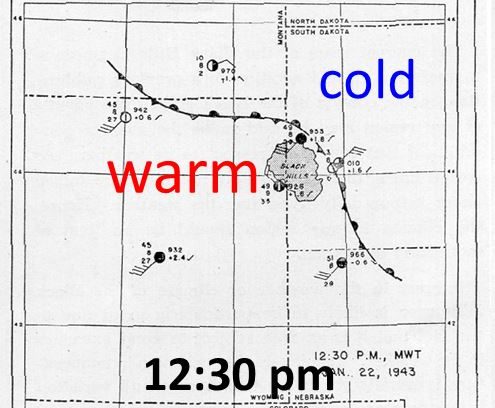
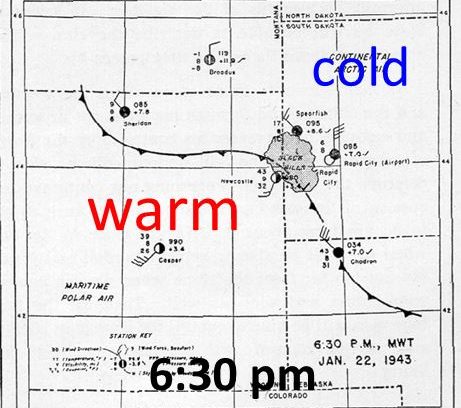 Spearfish holds another winter maximum temperature record as well. On January 19, 1921 the temperature soared to 79° F which is the hottest January temperature on record for the entire state.
More on Chinook Winds
Downslope or “foehn winds” are fairly common along mountain ranges and are often called “Chinook” winds or even “snow eater” because they can melt and evaporate snow rapidly with very warm and dry air.
Spearfish holds another winter maximum temperature record as well. On January 19, 1921 the temperature soared to 79° F which is the hottest January temperature on record for the entire state.
More on Chinook Winds
Downslope or “foehn winds” are fairly common along mountain ranges and are often called “Chinook” winds or even “snow eater” because they can melt and evaporate snow rapidly with very warm and dry air.
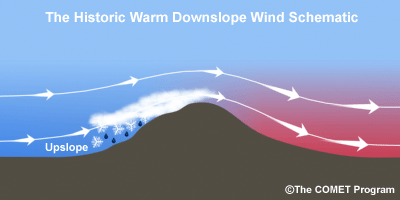 When moist winds from the west are forced to rise over higher elevations of a mountain range, the air cools, moisture in the air is condensed and falls out as precipitation. The phase change from water vapor to liquid or frozen water releases heat into the air. As stated, when the air is forced to rise over higher elevations it expands and cools. That cooling is somewhat hindered by the latent heat released by condensation. The air pushed up the windward side of the mountains will cool at the moist adiabatic lapse rate of around 3.5 °F / 1000 ft although this lapse rate varies depending on how much moisture there is. The moisture removed from the air will leave it much drier for it’s trip to lower elevations on the leeward side of the mountains. The dried air then descends on the leeward side of the mountains, warming at the dry adiabatic rate of 5.5 °F / 1000 ft. This just means that the heat added to the air on its way up through condensation will be added to the warmth as it descends to lower elevations.
Air temperatures west of the mountains can be much colder than locations east on the plains once the down slope is underway.
Mike Morrison
When moist winds from the west are forced to rise over higher elevations of a mountain range, the air cools, moisture in the air is condensed and falls out as precipitation. The phase change from water vapor to liquid or frozen water releases heat into the air. As stated, when the air is forced to rise over higher elevations it expands and cools. That cooling is somewhat hindered by the latent heat released by condensation. The air pushed up the windward side of the mountains will cool at the moist adiabatic lapse rate of around 3.5 °F / 1000 ft although this lapse rate varies depending on how much moisture there is. The moisture removed from the air will leave it much drier for it’s trip to lower elevations on the leeward side of the mountains. The dried air then descends on the leeward side of the mountains, warming at the dry adiabatic rate of 5.5 °F / 1000 ft. This just means that the heat added to the air on its way up through condensation will be added to the warmth as it descends to lower elevations.
Air temperatures west of the mountains can be much colder than locations east on the plains once the down slope is underway.
Mike Morrison
 That day started out very cold in Spearfish, and at 7:30 am MST the temperature recorded was -4°F.
At that time Chinook winds picked up speed and two minutes later at 7:32 am the temperature rose to +45° F. This was a 49° increase in just two minutes that is a record that still stands.
Temperatures continued to rise and at 9:00 am the temperature reached +54° F. As the chinook winds died down and 27 minutes later the temperature dropped 58° F back to -4° F.
The rapid temperature fluctuation that day caused glass windows to crack and instantly frosted car windows.
That day started out very cold in Spearfish, and at 7:30 am MST the temperature recorded was -4°F.
At that time Chinook winds picked up speed and two minutes later at 7:32 am the temperature rose to +45° F. This was a 49° increase in just two minutes that is a record that still stands.
Temperatures continued to rise and at 9:00 am the temperature reached +54° F. As the chinook winds died down and 27 minutes later the temperature dropped 58° F back to -4° F.
The rapid temperature fluctuation that day caused glass windows to crack and instantly frosted car windows.


 Spearfish holds another winter maximum temperature record as well. On January 19, 1921 the temperature soared to 79° F which is the hottest January temperature on record for the entire state.
More on Chinook Winds
Downslope or “foehn winds” are fairly common along mountain ranges and are often called “Chinook” winds or even “snow eater” because they can melt and evaporate snow rapidly with very warm and dry air.
Spearfish holds another winter maximum temperature record as well. On January 19, 1921 the temperature soared to 79° F which is the hottest January temperature on record for the entire state.
More on Chinook Winds
Downslope or “foehn winds” are fairly common along mountain ranges and are often called “Chinook” winds or even “snow eater” because they can melt and evaporate snow rapidly with very warm and dry air.
 When moist winds from the west are forced to rise over higher elevations of a mountain range, the air cools, moisture in the air is condensed and falls out as precipitation. The phase change from water vapor to liquid or frozen water releases heat into the air. As stated, when the air is forced to rise over higher elevations it expands and cools. That cooling is somewhat hindered by the latent heat released by condensation. The air pushed up the windward side of the mountains will cool at the moist adiabatic lapse rate of around 3.5 °F / 1000 ft although this lapse rate varies depending on how much moisture there is. The moisture removed from the air will leave it much drier for it’s trip to lower elevations on the leeward side of the mountains. The dried air then descends on the leeward side of the mountains, warming at the dry adiabatic rate of 5.5 °F / 1000 ft. This just means that the heat added to the air on its way up through condensation will be added to the warmth as it descends to lower elevations.
Air temperatures west of the mountains can be much colder than locations east on the plains once the down slope is underway.
Mike Morrison
When moist winds from the west are forced to rise over higher elevations of a mountain range, the air cools, moisture in the air is condensed and falls out as precipitation. The phase change from water vapor to liquid or frozen water releases heat into the air. As stated, when the air is forced to rise over higher elevations it expands and cools. That cooling is somewhat hindered by the latent heat released by condensation. The air pushed up the windward side of the mountains will cool at the moist adiabatic lapse rate of around 3.5 °F / 1000 ft although this lapse rate varies depending on how much moisture there is. The moisture removed from the air will leave it much drier for it’s trip to lower elevations on the leeward side of the mountains. The dried air then descends on the leeward side of the mountains, warming at the dry adiabatic rate of 5.5 °F / 1000 ft. This just means that the heat added to the air on its way up through condensation will be added to the warmth as it descends to lower elevations.
Air temperatures west of the mountains can be much colder than locations east on the plains once the down slope is underway.
Mike MorrisonAll Weather News
More