Hurricane Forecast Models Get a Boost From New Satellite Data
Special Stories
17 Jun 2020 2:00 AM
[GOES-16 sees Hurricane Dorian moments before it made landfall over Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, on September 6, 2019. Credit: NOAA]
[Written by NOAA NESDIS] Hurricane forecast models got an upgrade this year, thanks to new satellite data. For the first time, GOES-16 (GOES-East) and GOES-17 (GOES-West) data are being fed into NOAA’s Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting (HWRF) computer model used to forecast the track and intensity of tropical cyclones.
NOAA is predicting an above-normal 2020 Atlantic hurricane season , which officially begins June 1. It’s already off to a busy start, with three named storms already and two forming prior to the official start of hurricane season. This is the sixth year in a row that a named storm has formed before June. The HWRF computer model is the operational backbone for hurricane track and intensity forecasts by NOAA’s National Hurricane Center (NHC) . The model uses data from satellites, aircraft, and radar. This year, high-resolution wind data from GOES-16 and GOES-17 is included in the model.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CdE3KyuElw8
[GOES-16 winds generated over Hurricane Irma on September 6, 2017, overlaid on GOES-16 visible imagery. Credit: NOAA]
The ability to characterize the wind fields in and around a hurricane is crucial to predicting future storm motion and intensity. Satellite wind estimates are determined by tracking clouds and moisture features in successive images.
Wind estimates from GOES-16 and GOES-17 define the wind flow over and around hurricanes, highlight the center of circulation, indicate the direction the storm will move, and provide valuable information on conditions that can lead to rapid intensification. The improved resolution and faster scanning from the satellites’ Advanced Baseline Imager enables higher quantity and quality of wind estimates than previously available.
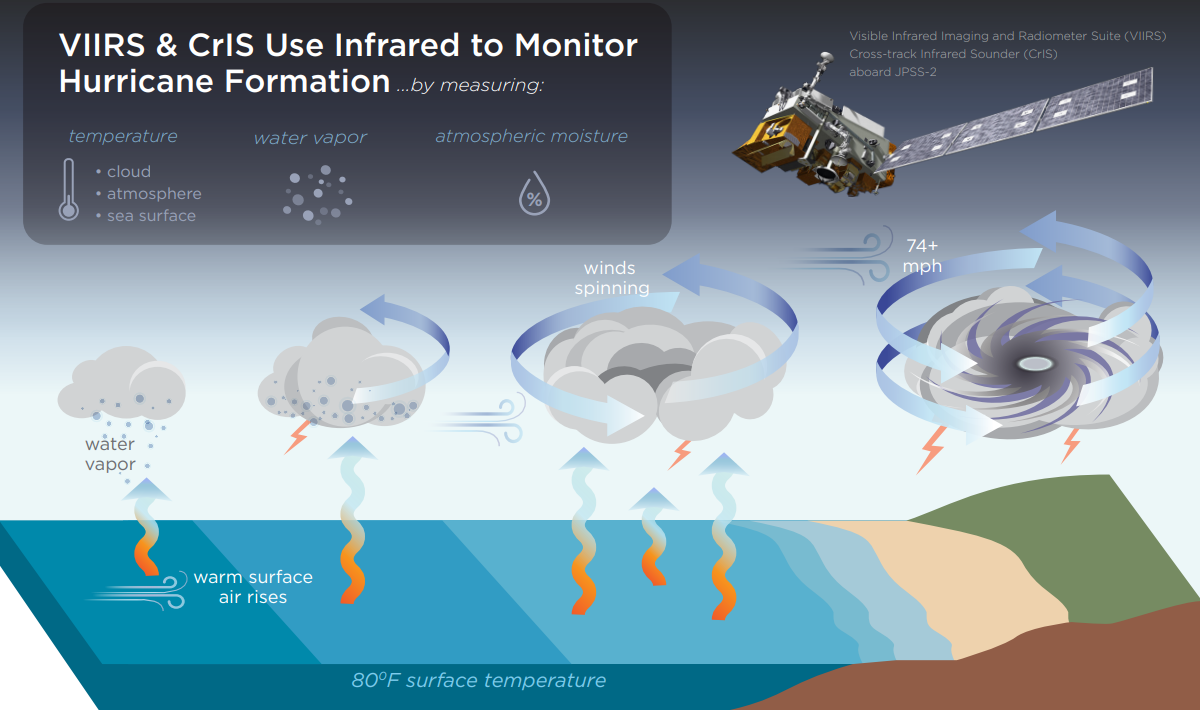 Also new to NOAA forecast models this year is data from NOAA’s COSMIC-2 and NOAA-20, NOAA/NASA Suomi-NPP, and Japan’s Himawari-8 satellites. And this new data is making a difference. “Our evaluation of assimilating new satellite data sets, including GOES-16 and GOES-17, into the operational HWRF model showed significant improvements in both track and intensity forecasts,” said Vijay Tallapragada, Modeling and Data Assimilation Branch Chief at NOAA’s Environmental Modeling Center. “The evaluation showed about 5% improvement for tracks and 8% for intensity in both the North Atlantic and Eastern Pacific hurricane basins.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
Also new to NOAA forecast models this year is data from NOAA’s COSMIC-2 and NOAA-20, NOAA/NASA Suomi-NPP, and Japan’s Himawari-8 satellites. And this new data is making a difference. “Our evaluation of assimilating new satellite data sets, including GOES-16 and GOES-17, into the operational HWRF model showed significant improvements in both track and intensity forecasts,” said Vijay Tallapragada, Modeling and Data Assimilation Branch Chief at NOAA’s Environmental Modeling Center. “The evaluation showed about 5% improvement for tracks and 8% for intensity in both the North Atlantic and Eastern Pacific hurricane basins.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
 Also new to NOAA forecast models this year is data from NOAA’s COSMIC-2 and NOAA-20, NOAA/NASA Suomi-NPP, and Japan’s Himawari-8 satellites. And this new data is making a difference. “Our evaluation of assimilating new satellite data sets, including GOES-16 and GOES-17, into the operational HWRF model showed significant improvements in both track and intensity forecasts,” said Vijay Tallapragada, Modeling and Data Assimilation Branch Chief at NOAA’s Environmental Modeling Center. “The evaluation showed about 5% improvement for tracks and 8% for intensity in both the North Atlantic and Eastern Pacific hurricane basins.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace Michaels
Also new to NOAA forecast models this year is data from NOAA’s COSMIC-2 and NOAA-20, NOAA/NASA Suomi-NPP, and Japan’s Himawari-8 satellites. And this new data is making a difference. “Our evaluation of assimilating new satellite data sets, including GOES-16 and GOES-17, into the operational HWRF model showed significant improvements in both track and intensity forecasts,” said Vijay Tallapragada, Modeling and Data Assimilation Branch Chief at NOAA’s Environmental Modeling Center. “The evaluation showed about 5% improvement for tracks and 8% for intensity in both the North Atlantic and Eastern Pacific hurricane basins.”
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More