The Science Behind Lake Effect Snow
Special Stories
20 Jan 2021 2:40 PM
Lake Effect Snow is a type of snow event we commonly see across the Great Lakes region during the Fall and Winter months. But for it to happen, we need the lakes to be unfrozen and a difference in temperature between the relatively warmer lake water and the colder air.
https://twitter.com/i/status/1351197660548513792
"When we have cold air move over the Great Lakes it helps to evaporate some of that warm, moist air which is a good contributing factor to seeing lake effect snow develop," said Karen Clark, Lead Meteorologist at the National Weather Service in Cleveland, OH.
https://twitter.com/NWSBUFFALO/status/1351847581433823235?s=20
Once the air rises, clouds will form and increase in size. As a result heavy, narrow bands of snow develop targeting isolated locations down wind of the lake.
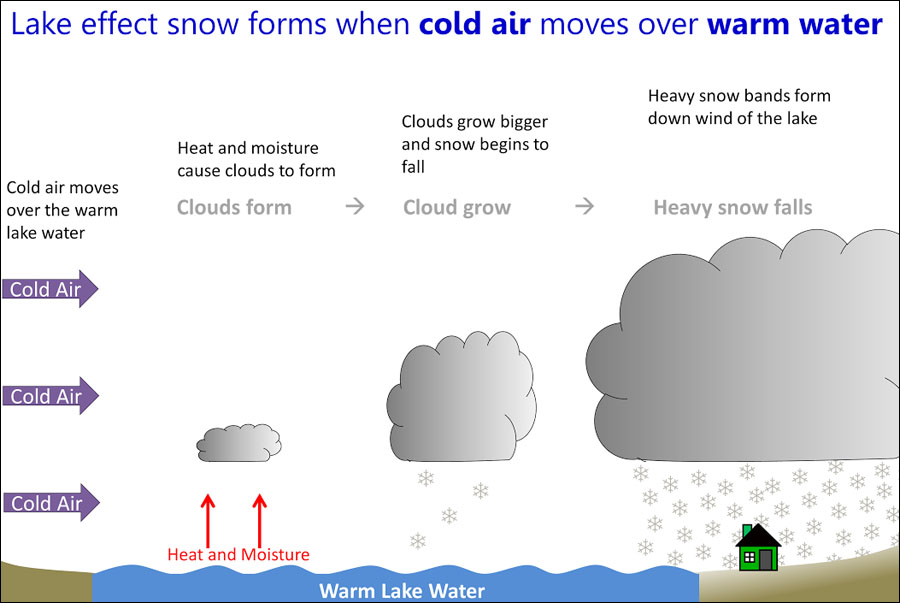 Courtesy: National Weather Service
"Lake effect snow bands are really interesting phenomenon," Clark said. "It’s not just like a typical snow event where you have widespread snow that’s the same intensity in all areas."
Depending on the wind direction and width of the band, some locations could experience very intense conditions while just a few miles away, sunny skies and calm weather.
READ MORE: Lake Effect Snow Bands
"Lake effect snow bands are prone to causing snowfall rates of 1-2” per hour, that’s something that we commonly see with some of our lake effect snow bands," Clark said.
And when the dynamics are just right, thunder and lightning can develop!
"When you start to overlap your strong, rising air, all that heat and moisture coming off the Great Lakes, we can result in thundersnow from time to time," Clark said. "And that’s typically a scenario where you are going to see higher snowfall rates with even 2 to maybe 3 inch per hour or higher snowfall rates within those bands.
But it’s not just throughout the Great Lakes that we get this type of weather event, even other lakes such as the Finger Lakes and the Great Salt Lake can have their own bands develop when conditions are right.
"Those lakes can provide a moisture source, they can provide a source for heat, and those are two contributing factors that we need," Clark said.
https://twitter.com/NWSSaltLakeCity/status/1111617793688887296?s=20
"What makes the Great Salt Lake unique is that it’s not frozen," said Christine Kruse, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in Salt Lake City, UT. "And so we can have that lake effect snow from periods as early as October all the way through the spring."
Courtesy: National Weather Service
"Lake effect snow bands are really interesting phenomenon," Clark said. "It’s not just like a typical snow event where you have widespread snow that’s the same intensity in all areas."
Depending on the wind direction and width of the band, some locations could experience very intense conditions while just a few miles away, sunny skies and calm weather.
READ MORE: Lake Effect Snow Bands
"Lake effect snow bands are prone to causing snowfall rates of 1-2” per hour, that’s something that we commonly see with some of our lake effect snow bands," Clark said.
And when the dynamics are just right, thunder and lightning can develop!
"When you start to overlap your strong, rising air, all that heat and moisture coming off the Great Lakes, we can result in thundersnow from time to time," Clark said. "And that’s typically a scenario where you are going to see higher snowfall rates with even 2 to maybe 3 inch per hour or higher snowfall rates within those bands.
But it’s not just throughout the Great Lakes that we get this type of weather event, even other lakes such as the Finger Lakes and the Great Salt Lake can have their own bands develop when conditions are right.
"Those lakes can provide a moisture source, they can provide a source for heat, and those are two contributing factors that we need," Clark said.
https://twitter.com/NWSSaltLakeCity/status/1111617793688887296?s=20
"What makes the Great Salt Lake unique is that it’s not frozen," said Christine Kruse, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in Salt Lake City, UT. "And so we can have that lake effect snow from periods as early as October all the way through the spring."
 Courtesy: National Weather Service
"Lake effect snow bands are really interesting phenomenon," Clark said. "It’s not just like a typical snow event where you have widespread snow that’s the same intensity in all areas."
Depending on the wind direction and width of the band, some locations could experience very intense conditions while just a few miles away, sunny skies and calm weather.
READ MORE: Lake Effect Snow Bands
"Lake effect snow bands are prone to causing snowfall rates of 1-2” per hour, that’s something that we commonly see with some of our lake effect snow bands," Clark said.
And when the dynamics are just right, thunder and lightning can develop!
"When you start to overlap your strong, rising air, all that heat and moisture coming off the Great Lakes, we can result in thundersnow from time to time," Clark said. "And that’s typically a scenario where you are going to see higher snowfall rates with even 2 to maybe 3 inch per hour or higher snowfall rates within those bands.
But it’s not just throughout the Great Lakes that we get this type of weather event, even other lakes such as the Finger Lakes and the Great Salt Lake can have their own bands develop when conditions are right.
"Those lakes can provide a moisture source, they can provide a source for heat, and those are two contributing factors that we need," Clark said.
https://twitter.com/NWSSaltLakeCity/status/1111617793688887296?s=20
"What makes the Great Salt Lake unique is that it’s not frozen," said Christine Kruse, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in Salt Lake City, UT. "And so we can have that lake effect snow from periods as early as October all the way through the spring."
Courtesy: National Weather Service
"Lake effect snow bands are really interesting phenomenon," Clark said. "It’s not just like a typical snow event where you have widespread snow that’s the same intensity in all areas."
Depending on the wind direction and width of the band, some locations could experience very intense conditions while just a few miles away, sunny skies and calm weather.
READ MORE: Lake Effect Snow Bands
"Lake effect snow bands are prone to causing snowfall rates of 1-2” per hour, that’s something that we commonly see with some of our lake effect snow bands," Clark said.
And when the dynamics are just right, thunder and lightning can develop!
"When you start to overlap your strong, rising air, all that heat and moisture coming off the Great Lakes, we can result in thundersnow from time to time," Clark said. "And that’s typically a scenario where you are going to see higher snowfall rates with even 2 to maybe 3 inch per hour or higher snowfall rates within those bands.
But it’s not just throughout the Great Lakes that we get this type of weather event, even other lakes such as the Finger Lakes and the Great Salt Lake can have their own bands develop when conditions are right.
"Those lakes can provide a moisture source, they can provide a source for heat, and those are two contributing factors that we need," Clark said.
https://twitter.com/NWSSaltLakeCity/status/1111617793688887296?s=20
"What makes the Great Salt Lake unique is that it’s not frozen," said Christine Kruse, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in Salt Lake City, UT. "And so we can have that lake effect snow from periods as early as October all the way through the spring."All Weather News
More